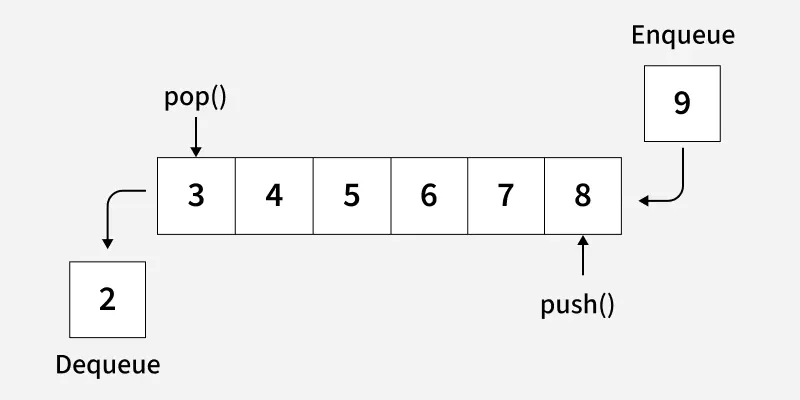
A queue is a container adapter that stores elements in FIFO (First In, First Out) order.
- The elements that are inserted first should be removed first.
- This is possible by inserting elements at one end (called back) and deleting them from the other end (called front) of the data structure.
 C++
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(10);
q.push(5);
// Accessing the front and back elements
cout << "Front element: " << q.front() << endl;
cout << "Back element: " << q.back() << endl;
// Removing an element from the front
q.pop();
cout << "Front element after pop: " << q.front() << endl;
return 0;
}
OutputFront element: 10
Back element: 5
Front element after pop: 5
Syntax
Queue is defined as the std::queue class template inside <queue> header file.
queue<T> q;
where,
- T: DataType of elements in the queue.
- q: Name assigned to the queue.
Basic Operations
Here are the basic operations that can be performed on a queue:
1. Inserting Elements
- New elements can only be inserted at back of the queue using push() function.
- The process of inserting elements in a queue is also called enqueue.
- Time complexity of insertion : O(1).
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
queue<int> q;
// Pushing elements into the queue
q.push(3);
q.push(4);
q.push(5);
return 0;
}
2. Accessing Elements
- Only the front and back elements of the queue can be accessed by using front() and back() functions respectively.
- Time complexity for accessing elements : O(1)
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(3);
q.push(4);
q.push(5);
// Accessing the front and back elements
cout << q.front() << endl;
cout << q.back();
return 0;
}
3. Deleting Elements
- Elements can only be deleted from the front of the queue using the
pop() function. - The process of deleting elements from a queue is also called dequeue.
- Time complexity for deletion : O(1)
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(3);
q.push(4);
q.push(5);
// Deleting elements from the front of the queue
q.pop();
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.front() << " ";
q.pop();
}
return 0;
}
4. empty()
- This checks whether the queue is empty.
- It returns true if the queue has no elements; otherwise, it returns false.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
queue<int> q;
if (q.empty())
{
cout << "Queue is empty " << endl;
}
q.push(100);
if (!q.empty())
{
cout << "Queue is not empty. Front element: " << q.front() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
OutputQueue is empty
Queue is not empty. Front element: 100
5.Size of queue
- The size() function in a queue returns the number of elements currently in the queue.
- It helps to determine how many items are stored without modifying the queue.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(10);
q.push(5);
cout << "Size of queue: " << q.size() << endl;
q.pop();
cout << "Size of queue: " << q.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
OutputSize of queue: 2
Size of queue: 1
Pseudo Traversal
- Since only the front and back element can be accessed in a queue, we cannot directly traverse it.
- On the other hand, we can create a copy of the queue, access the front element, and then delete it, and continue this process until the copied queue is empty, we can effectively traverse all the elements of the queue.
- Time complexity for traversal : O(n)
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(3);
q.push(4);
q.push(5);
// Create a copy
queue<int> temp(q);
while (!temp.empty())
{
cout << temp.front() << " ";
temp.pop();
}
return 0;
}
All Member Functions
Following is the list of all member functions of std::queue class in C++:
Functions | Description |
|---|
front() | Access the front element of the queue. |
|---|
back() | Access the end element of the queue. |
|---|
empty() | Check whether a queue is empty or not. |
|---|
size() | Returns the number of elements in the queue. |
|---|
push() | Adding an element at the back of the queue. |
|---|
push_range() | Adding multiple elements at the end of queue. |
|---|
emplace() | Add the constructs element in top of the queue. |
|---|
pop() | Delete the front element of the queue. |
|---|
swap() | Swap two queues. |
|---|
Explore
C++ Basics
Core Concepts
OOP in C++
Standard Template Library(STL)
Practice & Problems