GATE DA 2024
Question 1
Consider the two neural networks (NNs) shown in Figures 1 and 2, with 𝑅𝑒𝐿𝑈 activation (𝑅𝑒𝐿𝑈(𝑧) = max{0, 𝑧}, ∀𝑧 ∈ ℝ). ℝ denotes the set of real numbers. The connections and their corresponding weights are shown in the Figures. The biases at every neuron are set to 0. For what values of 𝑝, 𝑞, 𝑟 in Figure 2 are the two NNs equivalent, when 𝑥1 ,𝑥2 , 𝑥3 are positive?
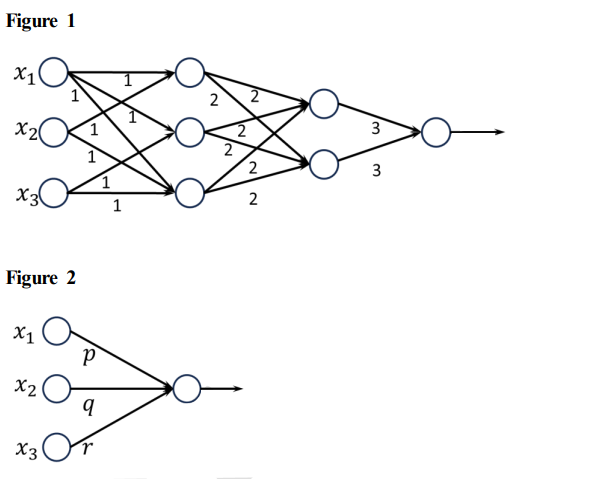
(A) 𝑝 = 36, 𝑞 = 24,𝑟 = 24
(B) 𝑝 = 24, 𝑞 = 24,𝑟 = 36
(C) 𝑝 = 18, 𝑞 = 36,𝑟 = 24
(D) 𝑝 = 36, 𝑞 = 36,𝑟 = 36
Question 2
Three fair coins are tossed independently. T is the event that two or more tosses result in heads. S is the event that two or more tosses result in tails. What is the probability of the event that (T ∧ S) ?
0
0.5
0.25
1
Question 3
Consider the following Python function:1
def fun(D, s1, s2):
if s1 < s2:
D[s1], D[s2] = D[s2], D[s1]
fun(D, s1+1, s2-
What does this Python function fun() do? Select the ONE appropriate option below.
It finds the smallest element in D from index s1 to s2, both inclusive.
It performs a merge sort in-place on this list D between indices s1 and s2, both inclusive.
It reverses the list D between indices s1 and s2, both inclusive
It swaps the elements in D at indices s1 and s2, and leaves the remaining elements unchanged.
Question 4
Let F(n) denote the maximum number of comparisons made while searching for an entry in a sorted array of size 𝑛 using binary search. Which ONE of the following options is TRUE?
F(n)=F(⌊n/2⌋)+1
F(n)=F(⌊n/2⌋)+F(⌈n/2⌉)
F(n)=F(⌊n/2⌋)
F(n)=F(n-1)+1
Question 5
Consider the function computeS(X) whose pseudocode is given below:
computeS(X)
𝑆[1] ← 1
for 𝑖 ←2 to length(X)
𝑆[𝑖] ← 1
if 𝑋[𝑖 − 1] ≤ 𝑋[𝑖]
𝑆[𝑖] ← 𝑆[𝑖] + 𝑆[𝑖 − 1]
end if
end for
return S
which ONE of the following values is returned by the function computeS(x)
for X=[6,3,5,4,10]?
[1,1,2,3,4]
[1,1,2,3,3]
[1,1,2,1,2]
[1,1,2,1,5]
Question 6
Consider the following python code:
def count(child_dict, i):
if i not in child_dict.keys():
return 1
ans = 1
for j in child_dict[i]:
ans += count(child_dict, j)
return ans
child_dict = dict()
child_dict[0] = [1,2]
child_dict[1] = [3,4,5]
child_dict[2] = [6,7,8]
print(count(child_dict,0))
Which ONE of the following is the output of this code?
6
1
8
9
Question 7
A fair six-sided die (with faces numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) is repeatedly thrown Independently. What is the expected number of times the die is thrown until two consecutive throws of even numbers are seen?
2
4
6
8
Question 8
[Tex]\text{Let } M = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 3 & 1 & 3 \\ 4 & 3 & 6 \end{bmatrix}[/Tex]. [Tex]\text{Find } \det(M^2 + 12M)[/Tex]
0
1
2
3
Question 9
Consider sorting the following array of integers in ascending order using an in-place Quicksort algorithm that uses the last element as the pivot.
| 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 |
The minimum number of swaps perfoemed during this quicksort ?
0
1
2
4
Question 10
Consider the following tree traversals on a full binary tree:
1.PreOrder
2.Inorder
3.PostOrder
Which of the following traversal options is/are suffiecient to uniquely reconstruct the full Binary Tree?
(i) and (ii)
(ii) and (iii)
(i) and (iii)
(ii) only
There are 64 questions to complete.