Retrofit with Kotlin Coroutine in Android
Last Updated :
02 Jan, 2025
Retrofit is a type-safe http client which is used to retrieve, update and delete the data from web services. Nowadays retrofit library is popular among the developers to use the API key. The Kotlin team defines coroutines as “lightweight threads”. They are sort of tasks that the actual threads can execute. Coroutines were added to Kotlin in version 1.3 and are based on established concepts from other languages. Kotlin coroutines introduce a new style of concurrency that can be used on Android to simplify async code. In this article, we will learn about retrofit using Kotlin coroutine. So we will be using Retrofit for network requests. Retrofit is a very popular library used for working APIs and very commonly used as well. We will learn it by making a simple app using an API to get some data using Retrofit.
Step-by-Step Implementation
Step 1: Create a New Project
To create a new project in Android Studio please refer to How to Create/Start a New Project in Android Studio .
Step 2: Add dependency
Navigate to the Gradle Scripts > build.gradle(Module:app) and add the below dependency in the dependencies section.
// retrofit
implementation 'com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.9.0'
// GSON
implementation 'com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.9.0'
// coroutine
implementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:1.5.2'
implementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.5.2'
We are using GSON to convert JSON to kotlin(Java) object. We will add these dependencies in build.gradle file inside our project.
Step 3: We will use the below API
https://quotable.io/quotes?page=1
 Figure 01
Figure 01 So our JSON response will look like this Figure01.
Step 4 : Then we will create data classes according to JSON response
In JSON response we have 2 JSON objects, So we will create 2 data class
- QuoteList
- Results
Kotlin
// data class QuoteList
// according to JSON response
package com.ayush.retrofitexample
data class QuoteList(
val count: Int,
val lastItemIndex: Int,
val page: Int,
val results: List<Result>,
val totalCount: Int,
val totalPages: Int
)
2nd data class
Kotlin
package com.ayush.retrofitexample
data class Result(
val _id: String,
val author: String,
val authorSlug: String,
val content: String,
val dateAdded: String,
val dateModified: String,
val length: Int,
val tags: List<String>
)
Step 5 : We will create a Retrofit interface to add the endpoints of the URL (quotes in our case is the endpoint)
Kotlin
// Retrofit interface
package com.ayush.retrofitexample
import retrofit2.Response
import retrofit2.http.GET
import retrofit2.http.Query
interface QuotesApi {
@GET("/quotes")
suspend fun getQuotes() : Response<QuoteList>
}
Step 6 : We will create a new file to get the Retrofit object
In this file, we will have a function that will return the Retrofit object.
Kotlin
package com.ayush.retrofitexample
import retrofit2.Retrofit
import retrofit2.converter.gson.GsonConverterFactory
object RetrofitHelper {
val baseUrl = "https://quotable.io/"
fun getInstance(): Retrofit {
return Retrofit.Builder().baseUrl(baseUrl)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
// we need to add converter factory to
// convert JSON object to Java object
.build()
}
}
Step 7 : Now we will link the Retrofit object and Retrofit interface file in MainActivity
Kotlin
package com.ayush.retrofitexample
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.util.Log
import kotlinx.coroutines.GlobalScope
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
import retrofit2.create
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val quotesApi = RetrofitHelper.getInstance().create(QuotesApi::class.java)
// launching a new coroutine
GlobalScope.launch {
val result = quotesApi.getQuotes()
if (result != null)
// Checking the results
Log.d("ayush: ", result.body().toString())
}
}
}
Step 8 : Add Internet permission in the manifests file
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"></uses-permission>
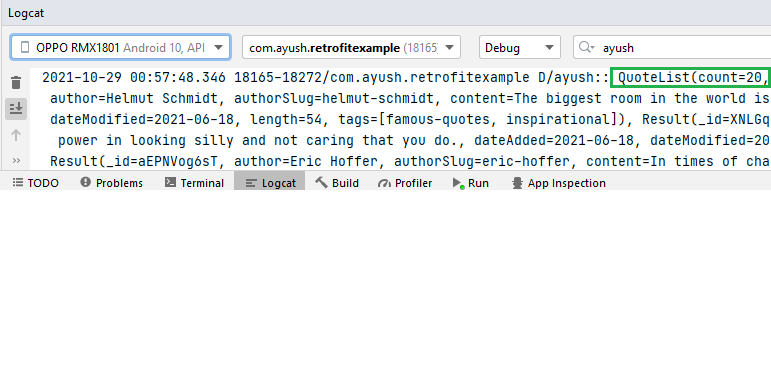
Results: we can check the logcat window. We can see the result in the green box.
Output:
Similar Reads
Introduction to Retrofit in Android Retrofit is a type-safe HTTP client for Android, developed by Square. It simplifies network operations by allowing developers to define REST API interactions using Java/Kotlin interfaces. It supports various request methods like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, and PATCH while enabling seamless integration w
5 min read
Unit Testing of ViewModel with Kotlin Coroutines and LiveData in Android The official documentation says that coroutines are lightweight threads. By lightweight, it means that creating coroutines doesn’t allocate new threads. Instead, they use predefined thread pools and smart scheduling for the purpose of which task to execute next and which tasks later. In this article
4 min read
Android - JSON Parsing using Retrofit Library with Kotlin JSON is a format with the help of which we can exchange the data from the server within our application or a website. For accessing this data from the server within android applications. There are several libraries that are available such as Volley and Retrofit. In this article, we will take a look
6 min read
withContext in Kotlin Coroutines Prerequisite: Kotlin Coroutines on AndroidLaunch vs Async in Kotlin Coroutines It is known that async and launch are the two ways to start the coroutine. Since It is known that async is used to get the result back, & should be used only when we need the parallel execution, whereas the launch is
3 min read
runBlocking in Kotlin Coroutines with Example Prerequisite: Kotlin Coroutines on AndroidSuspend Function In Kotlin Coroutines As it is known that when the user calls the delay() function in any coroutine, it will not block the thread in which it is running, while the delay() function is called one can do some other operations like updating UI a
5 min read