Reverse alternate K nodes in a Singly Linked List
Last Updated :
04 Sep, 2024
Given a linked list, The task is to reverse alternate k nodes. If the number of nodes left at the end of the list is fewer than k, reverse these remaining nodes or leave them in their original order, depending on the alternation pattern.
Example:
Input: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> NULL, k = 2
Output: 2 -> 1 -> 3 -> 4 -> 6 -> 5 -> NULL.
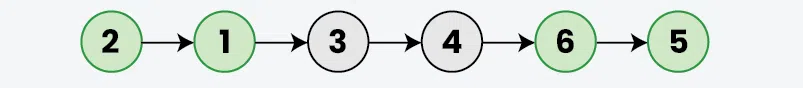
Explanation :The nodes are reversed alternatively after 2 nodes.
Input: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> NULL, k = 3
Output: 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 8 -> 7-> NULL.

Explanation :The nodes are reversed alternatively after 3 nodes.
[Expected Approach - 1] Using Recursion - O(n) Time and O(n) Space:
The idea is to use recursive approach which involves reversing the first k nodes , skipping the subsequent k nodes, and then applying the same logic to the remaining portion of the list. By recursively calling the function on each segment, we ensure that the alternation pattern is maintained.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to reverse alternate
// k nodes in a linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
};
// Reverses alternate k nodes and returns
// the pointer to the new head node
Node* kAltReverse(Node* head, int k) {
Node* curr = head;
Node* next = NULL;
Node* prev = NULL;
int count = 0;
// Reverse the first k nodes of the linked list
while (curr != NULL && count < k) {
next = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
count++;
}
// Now head points to the kth node.
// So change next of head to (k+1)th node
if (head != NULL) {
head->next = curr;
}
// Skip the next k nodes
count = 0;
while (count < k - 1 && curr != NULL) {
curr = curr->next;
count++;
}
// Recursively call for the list
// starting from curr->next
if (curr != NULL) {
curr->next = kAltReverse(curr->next, k);
}
// prev is the new head of the input list
return prev;
}
void printList(Node* node) {
Node* curr = node;
while (curr != NULL) {
cout << curr->data << " ";
curr = curr->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
// Hardcoded linked list: 1->2->3->4->5->6
Node* head = new Node(1);
head->next = new Node(2);
head->next->next = new Node(3);
head->next->next->next = new Node(4);
head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5);
head->next->next->next->next->next = new Node(6);
head = kAltReverse(head, 2);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// C program to reverse alternate
// k nodes in a linked list
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// Reverses alternate k nodes and returns
// the pointer to the new head node
struct Node* kAltReverse(struct Node* head, int k) {
struct Node* curr = head;
struct Node* next = NULL;
struct Node* prev = NULL;
int count = 0;
// Reverse the first k nodes of the linked list
while (curr != NULL && count < k) {
next = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
count++;
}
// Now head points to the kth node.
// So change next of head to (k+1)th node
if (head != NULL) {
head->next = curr;
}
// Skip the next k nodes
count = 0;
while (count < k - 1 && curr != NULL) {
curr = curr->next;
count++;
}
// Recursively call for the list
// starting from curr->next
if (curr != NULL) {
curr->next = kAltReverse(curr->next, k);
}
// prev is the new head of the input list
return prev;
}
void printList(struct Node* node) {
struct Node* curr = node;
while (curr != NULL) {
printf("%d ", curr->data);
curr = curr->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
struct Node* createNode(int x) {
struct Node* node =
(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = x;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
int main() {
// Hardcoded linked list: 1->2->3->4->5->6
struct Node* head = createNode(1);
head->next = createNode(2);
head->next->next = createNode(3);
head->next->next->next = createNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = createNode(5);
head->next->next->next->next->next = createNode(6);
head = kAltReverse(head, 2);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// Java program to reverse alternate
// k nodes in a linked list
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
class GfG {
// Reverses alternate k nodes and returns
// the pointer to the new head node
static Node kAltReverse(Node head, int k) {
Node curr = head;
Node next = null;
Node prev = null;
int count = 0;
// Reverse the first k nodes of the linked list
while (curr != null && count < k) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
count++;
}
// Now head points to the kth node.
// So change next of head to (k+1)th node
if (head != null) {
head.next = curr;
}
// Skip the next k nodes
count = 0;
while (count < k - 1 && curr != null) {
curr = curr.next;
count++;
}
// Recursively call for the list
// starting from curr->next
if (curr != null) {
curr.next = kAltReverse(curr.next, k);
}
// prev is the new head of
// the input list
return prev;
}
static void printList(Node node) {
Node curr = node;
while (curr != null) {
System.out.print(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Hardcoded linked list: 1->2->3->4->5->6
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head = kAltReverse(head, 2);
printList(head);
}
}
# Python program to reverse alternate
# k nodes in a linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
# Reverses alternate k nodes and returns
# the pointer to the new head node
def kAltReverse(head, k):
curr = head
next = None
prev = None
count = 0
# Reverse the first k nodes of the linked list
while curr is not None and count < k:
next = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
count += 1
# Now head points to the kth node.
# So change next of head to (k+1)th node
if head is not None:
head.next = curr
# Skip the next k nodes
count = 0
while count < k - 1 and curr is not None:
curr = curr.next
count += 1
# Recursively call for the list
# starting from curr->next
if curr is not None:
curr.next = kAltReverse(curr.next, k)
# prev is the new head of the input list
return prev
def printList(node):
curr = node
while curr is not None:
print(curr.data, end=" ")
curr = curr.next
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Hardcoded linked list: 1->2->3->4->5->6
head = Node(1)
head.next = Node(2)
head.next.next = Node(3)
head.next.next.next = Node(4)
head.next.next.next.next = Node(5)
head.next.next.next.next.next = Node(6)
head = kAltReverse(head, 2)
printList(head)
// C# program to reverse alternate
// k nodes in a linked list
using System;
class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
class GfG {
// Reverses alternate k nodes and returns
// the pointer to the new head node
static Node kAltReverse(Node head, int k) {
Node curr = head;
Node next = null;
Node prev = null;
int count = 0;
// Reverse the first k nodes of the linked list
while (curr != null && count < k) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
count++;
}
// Now head points to the kth node.
// So change next of head to (k+1)th node
if (head != null) {
head.next = curr;
}
// Skip the next k nodes
count = 0;
while (count < k - 1 && curr != null) {
curr = curr.next;
count++;
}
// Recursively call for the list
// starting from curr->next
if (curr != null) {
curr.next = kAltReverse(curr.next, k);
}
// prev is the new head of the input list
return prev;
}
static void printList(Node node) {
Node curr = node;
while (curr != null) {
Console.Write(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
// Hardcoded linked list: 1->2->3->4->5->6
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head = kAltReverse(head, 2);
printList(head);
}
}
// JavaScript program to reverse alternate k
// nodes in a linked list
class Node {
constructor(x) {
this.data = x;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Reverses alternate k nodes and returns
// the pointer to the new head node
function kAltReverse(head, k) {
let curr = head;
let next = null;
let prev = null;
let count = 0;
// Reverse the first k nodes of the
// linked list
while (curr !== null && count < k) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
count++;
}
// Now head points to the kth node.
// So change next of head to (k+1)th node
if (head !== null) {
head.next = curr;
}
// Skip the next k nodes
count = 0;
while (count < k - 1 && curr !== null) {
curr = curr.next;
count++;
}
// Recursively call for the list
// starting from curr->next
if (curr !== null) {
curr.next = kAltReverse(curr.next, k);
}
// prev is the new head of
// the input list
return prev;
}
function printList(node) {
let curr = node;
while (curr !== null) {
console.log(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
console.log();
}
// Hardcoded linked list: 1->2->3->4->5->6
let head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head = kAltReverse(head, 2);
printList(head);
Time Complexity: O(n) , where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
[Expected Approach - 2] Using Iterative Method - O(n) Time and O(1) Space:
The idea is similar to the recursive approach , instead we are traversing the linkedlist iteratively. We'll keep reversing the k nodes and skiping the next k nodes untill we still have nodes to process.
Step by Step Approach:
- Initialize Pointers, prevTail (Tail of the previous segment) , curr (Current node being processed) and rev (Flag to indicate if the segment should be reversed).
- Traverse the list using the curr pointer while there are still nodes to process:
- If rev flag is True , reverse the next k nodes, then connect the reversed segment to prevTail. if the prevTail pointer is NULL , the actual head pointer will point to prevtail representing the newhead of final list.
- else skip the next k nodes by updating prevTail.
- Toggle the rev flag to perform alternate reversal.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to reverse alternate k nodes
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *next;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
};
Node *kAltReverse(Node *head, int k) {
// Pointer to the tail of the
// previous segment
Node *prevTail = NULL;
bool rev = true;
Node *curr = head;
while (curr != NULL) {
// Reverse the next k nodes
if (rev == true) {
// Mark the head of the
// current segment
Node *segHead = curr;
Node *prev = NULL;
// Reverse the current segment of k nodes
for (int i = 0; i < k && curr != NULL; i++) {
Node *nxt = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nxt;
}
// Update the head of the list if this
// is the first segment
if (prevTail == NULL) {
head = prev;
}
else {
// Link previous segment with the
// current reversed segment
prevTail->next = prev;
}
// Update the tail of the current segment
prevTail = segHead;
rev = false;
}
else {
// Skip the next k nodes without reversing
prevTail->next = curr;
for (int i = 0; i < k && curr != NULL; i++) {
prevTail = curr;
curr = curr->next;
}
rev = true;
}
}
return head;
}
void printList(Node *node) {
Node *curr = node;
while (curr != NULL) {
cout << curr->data << " ";
curr = curr->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
// Hardcoded linked list:
// 1->2->3->4->5->6
Node *head = new Node(1);
head->next = new Node(2);
head->next->next = new Node(3);
head->next->next->next = new Node(4);
head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5);
head->next->next->next->next->next = new Node(6);
head = kAltReverse(head, 2);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// C program to reverse alternate k nodes
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
struct Node *kAltReverse(struct Node *head, int k) {
// Pointer to the tail of the
// previous segment
struct Node *prevTail = NULL;
int rev = 1;
struct Node *curr = head;
while (curr != NULL) {
// Reverse the next k nodes
if (rev == 1) {
// Mark the head of the current segment
struct Node *segHead = curr;
struct Node *prev = NULL;
// Reverse the current segment of k nodes
for (int i = 0; i < k && curr != NULL; i++) {
struct Node *nxt = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nxt;
}
// Update the head of the list if
// this is the first segment
if (prevTail == NULL) {
head = prev;
}
else {
// Link previous segment with the
// current reversed segment
prevTail->next = prev;
}
// Update the tail of the current segment
prevTail = segHead;
rev = 0;
}
else {
// Skip the next k nodes without reversing
prevTail->next = curr;
for (int i = 0; i < k && curr != NULL; i++) {
prevTail = curr;
curr = curr->next;
}
rev = 1;
}
}
return head;
}
void printList(struct Node *node) {
struct Node *curr = node;
while (curr != NULL) {
printf("%d ", curr->data);
curr = curr->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
struct Node *createNode(int x) {
struct Node *node =
(struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = x;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
int main() {
// Hardcoded linked list: 1->2->3->4->5->6
struct Node *head = createNode(1);
head->next = createNode(2);
head->next->next = createNode(3);
head->next->next->next = createNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = createNode(5);
head->next->next->next->next->next = createNode(6);
head = kAltReverse(head, 2);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// Java program to reverse alternate
// k nodes in a linked list
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
class GfG {
static Node kAltReverse(Node head, int k) {
// Pointer to the tail of the
// previous segment
Node prevTail = null;
boolean rev = true;
Node curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
// Reverse the next k nodes
if (rev == true) {
// Mark the head of the
// current segment
Node segHead = curr;
Node prev = null;
// Reverse the current
// segment of k nodes
for (int i = 0; i < k && curr != null; i++) {
Node nxt = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nxt;
}
// Update the head of the list
// if this is the first segment
if (prevTail == null) {
head = prev;
}
else {
// Link previous segment with the
// current reversed segment
prevTail.next = prev;
}
// Update the tail of the
// current segment
prevTail = segHead;
rev = false;
}
else {
// Skip the next k nodes
// without reversing
prevTail.next = curr;
for (int i = 0; i < k && curr != null;
i++) {
prevTail = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
rev = true;
}
}
return head;
}
static void printList(Node node) {
Node curr = node;
while (curr != null) {
System.out.print(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Hardcoded linked list: 1->2->3->4->5->6
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head = kAltReverse(head, 2);
printList(head);
}
}
# Python program to reverse alternate k nodes
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
def kAltReverse(head, k):
# Pointer to the tail of the
# previous segment
prev_tail = None
rev = True
curr = head
while curr:
# Reverse the next k nodes
if rev == True:
# Mark the head of the current segment
seg_head = curr
prev = None
# Reverse the current segment of k nodes
for _ in range(k):
if curr is None:
break
nxt = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = nxt
# Update the head of the list
# if this is the first segment
if prev_tail is None:
head = prev
else:
# Link previous segment with
# the current reversed segment
prev_tail.next = prev
# Update the tail of the current segment
prev_tail = seg_head
rev = False
else:
# Skip the next k nodes without reversing
prev_tail.next = curr
for _ in range(k):
if curr is None:
break
prev_tail = curr
curr = curr.next
rev = True
return head
def print_list(node):
curr = node
while curr:
print(curr.data, end=" ")
curr = curr.next
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Hardcoded linked list: 1->2->3->4->5->6
head = Node(1)
head.next = Node(2)
head.next.next = Node(3)
head.next.next.next = Node(4)
head.next.next.next.next = Node(5)
head.next.next.next.next.next = Node(6)
head = kAltReverse(head, 2)
print_list(head)
// C# program to reverse alternate k nodes
using System;
class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
class GfG {
static Node kAltReverse(Node head, int k) {
// Pointer to the tail of the previous segment
Node prevTail = null;
bool rev = true;
Node curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
// Reverse the next k nodes
if (rev == true) {
// Mark the head of the current segment
Node segHead = curr;
Node prev = null;
// Reverse the current segment of k nodes
for (int i = 0; i < k && curr != null;
i++) {
Node nxt = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nxt;
}
// Update the head of the list if this is
// the first segment
if (prevTail == null) {
head = prev;
}
else {
// Link previous segment with the
// current reversed segment
prevTail.next = prev;
}
// Update the tail of the current segment
prevTail = segHead;
rev = false;
}
else {
// Skip the next k nodes without reversing
prevTail.next = curr;
for (int i = 0; i < k && curr != null;
i++) {
prevTail = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
rev = true;
}
}
return head;
}
static void printList(Node node) {
Node curr = node;
while (curr != null) {
Console.Write(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
// Hardcoded linked list: 1->2->3->4->5->6
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head = kAltReverse(head, 2);
printList(head);
}
}
// Javascript program to reverse
// alternate k nodes
class Node {
constructor(x) {
this.data = x;
this.next = null;
}
}
function kAltReverse(head, k) {
// Pointer to the tail of
// the previous segment
let prevTail = null;
let rev = true;
let curr = head;
while (curr !== null) {
// Reverse the next k nodes
if (rev == true) {
// Mark the head of the current segment
let segHead = curr;
let prev = null;
// Reverse the current segment of k nodes
for (let i = 0; i < k && curr !== null; i++) {
let nxt = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nxt;
}
// Update the head of the list if this is the
// first segment
if (prevTail === null) {
head = prev;
}
else {
// Link previous segment with the current
// reversed segment
prevTail.next = prev;
}
// Update the tail of the current segment
prevTail = segHead;
rev = false;
}
else {
// Skip the next k nodes without reversing
prevTail.next = curr;
for (let i = 0; i < k && curr !== null; i++) {
prevTail = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
rev = true;
}
}
return head;
}
function printList(node) {
let curr = node;
while (curr !== null) {
console.log(curr.data);
curr = curr.next;
}
console.log();
}
// Hardcoded linked list: 1->2->3->4->5->6
let head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head = kAltReverse(head, 2);
printList(head);
Time Complexity: O(n) , where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Similar Reads
Reverse alternate K nodes in a Singly Linked List - Iterative Solution Given a linked list and an integer K, the task is to reverse every alternate K nodes.Examples: Input: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9 -> NULL, K = 3 Output: 3 2 1 4 5 6 9 8 7Input: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9 -> NULL, K =
12 min read
Javascript Program For Reversing Alternate K Nodes In A Singly Linked List Given a linked list, write a function to reverse every alternate k nodes (where k is an input to the function) in an efficient way. Give the complexity of your algorithm.Example: Inputs: 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->9->NULL and k = 3Output: 3->2->1->4->5->6->9
5 min read
Given a linked list, reverse alternate nodes and append at the end Given a linked list, reverse alternate nodes and append them to the end of the list. Extra allowed space is O(1) Examples: Input: 1->2->3->4->5->6 Output: 1->3->5->6->4->2 Explanation: Two lists are 1->3->5 and 2->4->6, reverse the 2nd list: 6->4->2. M
11 min read
XOR linked list: Reverse last K nodes of a Linked List Given a XOR Linked List and a positive integer K, the task is to reverse the last K nodes in the given XOR linked list. Examples: Input: LL: 7 <–> 6 <–> 8 <–> 11 <–> 3 <–> 1, K = 3Output: 7<–>6<–>8<–>1<–>3<–>11 Input: LL: 7 <–> 6 <
14 min read
C Program to reverse each node value in Singly Linked List A linked list is a linear collection of data elements, in which each node points to the next node. Unlike an array, it doesn't have upper limit and hence extremely useful. The task is to access value of each node of linked list and reverse them. Examples: Input : 56 87 12 49 35 Output : 65 78 21 94
2 min read