Search, Insert, and Delete in an Unsorted Array | Array Operations
Last Updated :
06 Sep, 2024
In this post, a program to search, insert, and delete operations in an unsorted array is discussed.
Search Operation:
In an unsorted array, the search operation can be performed by linear traversal from the first element to the last element.

Coding implementation of the search operation:
C++
// C++ program to implement linear
// search in unsorted array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to implement search operation
int findElement(int arr[], int n, int key)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == key)
return i;
// If the key is not found
return -1;
}
// Driver's Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 34, 10, 6, 40 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Using a last element as search element
int key = 40;
// Function call
int position = findElement(arr, n, key);
if (position == -1)
cout << "Element not found";
else
cout << "Element Found at Position: "
<< position + 1;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed
// by Akanksha Rai
// C program to implement linear
// search in unsorted array
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to implement search operation
int findElement(int arr[], int n, int key)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == key)
return i;
// If the key is not found
return -1;
}
// Driver's Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 34, 10, 6, 40 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Using a last element as search element
int key = 40;
// Function call
int position = findElement(arr, n, key);
if (position == -1)
printf("Element not found");
else
printf("Element Found at Position: %d",
position + 1);
return 0;
}
// Java program to implement linear
// search in unsorted arrays
class Main {
// Function to implement
// search operation
static int findElement(int arr[], int n, int key)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == key)
return i;
// If the key is not found
return -1;
}
// Driver's Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 12, 34, 10, 6, 40 };
int n = arr.length;
// Using a last element as search element
int key = 40;
// Function call
int position = findElement(arr, n, key);
if (position == -1)
System.out.println("Element not found");
else
System.out.println("Element Found at Position: "
+ (position + 1));
}
}
# Python program for searching in
# unsorted array
def findElement(arr, n, key):
for i in range(n):
if (arr[i] == key):
return i
# If the key is not found
return -1
# Driver's code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [12, 34, 10, 6, 40]
key = 40
n = len(arr)
# search operation
index = findElement(arr, n, key)
if index != -1:
print("Element Found at position: " + str(index + 1))
else:
print("Element not found")
# Thanks to Aditi Sharma for contributing
# this code
// C# program to implement linear
// search in unsorted arrays
using System;
class main {
// Function to implement
// search operation
static int findElement(int[] arr, int n, int key)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == key)
return i;
// If the key is not found
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 12, 34, 10, 6, 40 };
int n = arr.Length;
// Using a last element as
// search element
int key = 40;
int position = findElement(arr, n, key);
if (position == -1)
Console.WriteLine("Element not found");
else
Console.WriteLine("Element Found at Position: "
+ (position + 1));
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.
// Javascript program to implement linear
// search in unsorted array
// Function to implement search operation
function findElement( arr, n, key)
{
let i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == key)
return i;
return -1;
}
// Driver program
let arr = [12, 34, 10, 6, 40];
let n = arr.length;
// Using a last element as search element
let key = 40;
let position = findElement(arr, n, key);
if (position == - 1)
console.log("Element not found");
else
console.log("Element Found at Position: "
+ (position + 1));
<?php
// PHP program to implement linear
// search in unsorted array
// Function to implement
// search operation
function findElement($arr, $n, $key)
{
$i;
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
if ($arr[$i] == $key)
return $i;
// If the key is not found
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(12, 34, 10, 6, 40);
$n = sizeof($arr);
// Using a last element
// as search element
$key = 40;
$position = findElement($arr, $n, $key);
if ($position == - 1)
echo("Element not found");
else
echo("Element Found at Position: " . ($position + 1));
// This code is contributed by Ajit.
?>
OutputElement Found at Position: 5
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Insert Operation:
1. Insert at the end:
In an unsorted array, the insert operation is faster as compared to a sorted array because we don't have to care about the position at which the element is to be placed.
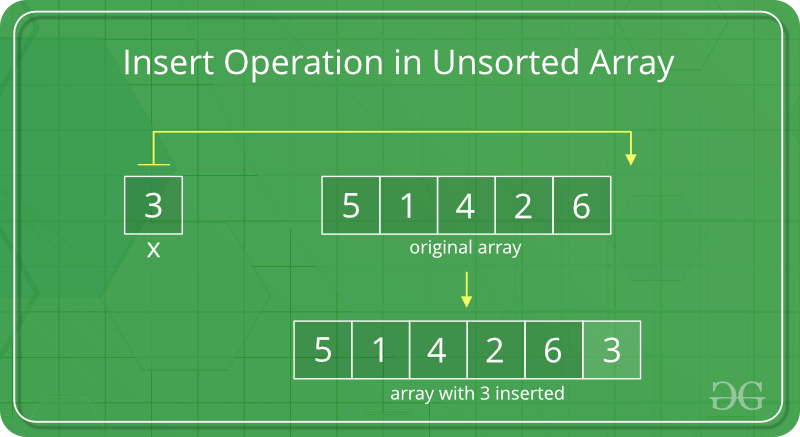
Coding implementation of inserting an element at the end:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Inserts a key in arr[] of the given capacity.
// n is the current size of arr[]. This
// function returns n + 1 if insertion
// is successful, else n.
int insertEnd(int arr[], int n, int key, int capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements if n is
// already more than or equal to capacity
if (n >= capacity)
return n;
arr[n] = key;
return (n + 1);
}
int main()
{
int arr[20] = { 12, 16, 20, 40, 50, 70 };
int capacity = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int n = 6;
int i, key = 26;
cout << "Before Insertion: ";
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
// Inserting key
n = insertEnd(arr, n, key, capacity);
cout << "\nAfter Insertion: ";
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
// C program to implement insert
// operation in an unsorted array.
#include <stdio.h>
// Inserts a key in arr[] of given capacity.
// n is current size of arr[]. This
// function returns n + 1 if insertion
// is successful, else n.
int insertEnd(int arr[], int n, int key, int capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements if n is
// already more than or equal to capacity
if (n >= capacity)
return n;
arr[n] = key;
return (n + 1);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[20] = { 12, 16, 20, 40, 50, 70 };
int capacity = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int n = 6;
int i, key = 26;
printf("\n Before Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
// Inserting key
n = insertEnd(arr, n, key, capacity);
printf("\n After Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}
// Java program to implement insert
// operation in an unsorted array.
class Main {
// Function to insert a given key in
// the array. This function returns n+1
// if insertion is successful, else n.
static int insertEnd(int arr[], int n, int key,
int capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements if n
// is already more than or equal to
// capacity
if (n >= capacity)
return n;
arr[n] = key;
return (n + 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = new int[20];
arr[0] = 12;
arr[1] = 16;
arr[2] = 20;
arr[3] = 40;
arr[4] = 50;
arr[5] = 70;
int capacity = 20;
int n = 6;
int i, key = 26;
System.out.print("Before Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
// Inserting key
n = insertEnd(arr, n, key, capacity);
System.out.print("\n After Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
# Python program for inserting
# an element in an unsorted array
# method to insert element
def insertEnd(arr, element):
arr.append(element)
# Driver's code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# declaring array and key to insert
arr = [12, 16, 20, 40, 50, 70]
key = 26
# array before inserting an element
print("Before Inserting: ")
print(arr)
# array after Inserting element
insertEnd(arr, key)
print("After Inserting: ")
print(arr)
# Thanks to Aditi Sharma for contributing
# this code
// C# program to implement insert
// operation in an unsorted array.
using System;
class main {
// Function to insert a given
// key in the array. This
// function returns n + 1
// if insertion is successful,
// else n.
static int insertEnd(int[] arr, int n, int key,
int capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements
// if n is already more than
// or equal to capacity
if (n >= capacity)
return n;
arr[n] = key;
return (n + 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = new int[20];
arr[0] = 12;
arr[1] = 16;
arr[2] = 20;
arr[3] = 40;
arr[4] = 50;
arr[5] = 70;
int capacity = 20;
int n = 6;
int i, key = 26;
Console.Write("Before Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
// Inserting key
n = insertEnd(arr, n, key, capacity);
Console.Write("After Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.
// Javascript program to implement insert
// operation in an unsorted array.
// Function to insert a given
// key in the array. This
// function returns n + 1
// if insertion is successful,
// else n.
function insertEnd(arr, n, key, capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements
// if n is already more than
// or equal to capacity
if (n >= capacity)
return n;
arr[n] = key;
return (n + 1);
}
let arr = new Array(20);
arr[0] = 12;
arr[1] = 16;
arr[2] = 20;
arr[3] = 40;
arr[4] = 50;
arr[5] = 70;
let capacity = 20;
let n = 6;
let i, key = 26;
console.log("Before Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
console.log(arr[i] + " ");
console.log("</br>");
// Inserting key
n = insertEnd(arr, n, key, capacity);
console.log("After Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
console.log(arr[i] + " ");
<?php
// PHP program to implement insert
// operation in an unsorted array.
// Inserts a key in arr[] of given
// capacity. n is current size of arr[].
// This function returns n + 1 if
// insertion is successful, else n.
function insertEnd(&$arr, $n, $key,
$capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements if n is
// already more than or equal to capacity
if ($n >= $capacity)
return $n;
array_push($arr, $key);
return ($n + 1);
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(12, 16, 20, 40, 50, 70);
$capacity = 20;
$n = 6;
$key = 26;
echo "Before Insertion: ";
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
echo $arr[$i] . " ";
// Inserting key
$n = insertEnd($arr, $n,
$key, $capacity);
echo "\nAfter Insertion: ";
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
echo $arr[$i] . " ";
// This code is contributed by
// Rajput-Ji
?>
Output Before Insertion: 12 16 20 40 50 70
After Insertion: 12 16 20 40 50 70 26
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
2. Insert at any position
Insert operation in an array at any position can be performed by shifting elements to the right, which are on the right side of the required position

Coding implementation of inserting an element at any position:
C++
// C++ Program to Insert an element
// at a specific position in an Array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to insert element
// at a specific position
void insertElement(int arr[], int n, int x, int pos)
{
// shift elements to the right
// which are on the right side of pos
for (int i = n - 1; i >= pos; i--)
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
arr[pos] = x;
}
// Driver's code
int main()
{
int arr[15] = { 2, 4, 1, 8, 5 };
int n = 5;
cout<<"Before insertion : ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
int x = 10, pos = 2;
// Function call
insertElement(arr, n, x, pos);
n++;
cout<<"After insertion : ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
return 0;
}
// C Program to Insert an element
// at a specific position in an Array
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to insert element
// at a specific position
void insertElement(int arr[], int n, int x, int pos)
{
// shift elements to the right
// which are on the right side of pos
for (int i = n - 1; i >= pos; i--)
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
arr[pos] = x;
}
// Driver's code
int main()
{
int arr[15] = { 2, 4, 1, 8, 5 };
int n = 5;
printf("Before insertion : ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
int x = 10, pos = 2;
// Function call
insertElement(arr, n, x, pos);
n++;
printf("After insertion : ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
// Java Program to Insert an element
// at a specific position in an Array
class GFG {
static void insertElement(int arr[], int n, int x,
int pos)
{
// shift elements to the right
// which are on the right side of pos
for (int i = n - 1; i >= pos; i--)
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
arr[pos] = x;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = new int[15];
arr[0] = 2;
arr[1] = 4;
arr[2] = 1;
arr[3] = 8;
arr[4] = 5;
int n = 5;
int x = 10, pos = 2;
System.out.print("Before Insertion: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
// Inserting key at specific position
insertElement(arr, n, x, pos);
n += 1;
System.out.print("\n\nAfter Insertion: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by syedsarfarazahammed
# python Program to Insert an element
# at a specific position in an Array
def insertElement(arr, n, x, pos) :
# shift elements to the right
# which are on the right side of pos
for i in range(n-1,pos-1,-1) :
arr[i + 1] = arr[i]
arr[pos] = x
# Driver's code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Declaring array and key to delete
# here -1 is for empty space
arr = [2, 4, 1, 8, 5, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1]
n = 5
print("Before insertion : ")
for i in range(0,n) :
print(arr[i],end=' ')
print("\n")
x = 10;
pos = 2;
# Function call
insertElement(arr, n, x, pos);
n+=1
print("After insertion : ")
for i in range(0,n) :
print(arr[i],end=' ')
#This Code is contributed by aditya942003patil
// C# program to implement insert
// operation in an unsorted array.
using System;
class main {
static void insertElement(int[] arr, int n, int x,
int pos)
{
// shift elements to the right
// which are on the right side of pos
for (int i = n - 1; i >= pos; i--)
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
arr[pos] = x;
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = new int[20];
arr[0] = 2;
arr[1] = 4;
arr[2] = 1;
arr[3] = 8;
arr[4] = 5;
int x = 10;
int n = 5;
int pos = 2;
Console.Write("Before Insertion: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
// Inserting key at specific position
insertElement(arr, n, x, pos);
n += 1;
Console.Write("\n\nAfter Insertion: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by sourabhdalal0001
// javascript Program to Insert an element
// at a specific position in an Array
function insertElement(arr, n, x, pos)
{
// shift elements to the right
// which are on the right side of pos
var i = n - 1;
for (i; i >= pos; i--)
{
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
}
arr[pos] = x;
}
var arr = Array(15).fill(0);
arr[0] = 2;
arr[1] = 4;
arr[2] = 1;
arr[3] = 8;
arr[4] = 5;
var n = 5;
var x = 10;
var pos = 2;
console.log("Before Insertion: ");
var i = 0;
for (i; i < n; i++)
{
console.log(arr[i] + " ");
}
// Inserting key at specific position
insertElement(arr, n, x, pos);
n += 1;
console.log("\n\nAfter Insertion: ");
i = 0;
for (i; i < n; i++)
{
console.log(arr[i] + " ");
}
<?php
$array = [2, 4, 1, 8, 5];
$element = 10;
function addElementAtPos($element, $position, &$array) {
// Shift elements to the right to make space for the new element
for ($i = count($array) - 1; $i >= $position; $i--) {
$array[$i + 1] = $array[$i];
}
// Insert the new element at the specified position
$array[$position] = $element;
}
echo 'Before: ' . implode(' ', $array) . "\n";
addElementAtPos($element, 2, $array);
echo 'After: ' . implode(' ', $array) . "\n";
?>
OutputBefore insertion : 2 4 1 8 5
After insertion : 2 4 10 1 8 5
Time complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Delete Operation:
In the delete operation, the element to be deleted is searched using the linear search, and then the delete operation is performed followed by shifting the elements.

C++
// C++ program to implement delete operation in a
// unsorted array
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// To search a key to be deleted
int findElement(int arr[], int n, int key);
// Function to delete an element
int deleteElement(int arr[], int n, int key)
{
// Find position of element to be deleted
int pos = findElement(arr, n, key);
if (pos == -1) {
cout << "Element not found";
return n;
}
// Deleting element
int i;
for (i = pos; i < n - 1; i++)
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
return n - 1;
}
// Function to implement search operation
int findElement(int arr[], int n, int key)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == key)
return i;
return -1;
}
// Driver's code
int main()
{
int i;
int arr[] = { 10, 50, 30, 40, 20 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int key = 30;
cout << "Array before deletion\n";
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
// Function call
n = deleteElement(arr, n, key);
cout << "\n\nArray after deletion\n";
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by shubhamsingh10
// C program to implement delete operation in a
// unsorted array
#include <stdio.h>
// To search a key to be deleted
int findElement(int arr[], int n, int key);
// Function to delete an element
int deleteElement(int arr[], int n, int key)
{
// Find position of element to be deleted
int pos = findElement(arr, n, key);
if (pos == -1) {
printf("Element not found");
return n;
}
// Deleting element
int i;
for (i = pos; i < n - 1; i++)
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
return n - 1;
}
// Function to implement search operation
int findElement(int arr[], int n, int key)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == key)
return i;
return -1;
}
// Driver's code
int main()
{
int i;
int arr[] = { 10, 50, 30, 40, 20 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int key = 30;
printf("Array before deletion\n");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
// Function call
n = deleteElement(arr, n, key);
printf("\nArray after deletion\n");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}
// Java program to implement delete
// operation in an unsorted array
class Main {
// function to search a key to
// be deleted
static int findElement(int arr[], int n, int key)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == key)
return i;
return -1;
}
// Function to delete an element
static int deleteElement(int arr[], int n, int key)
{
// Find position of element to be
// deleted
int pos = findElement(arr, n, key);
if (pos == -1) {
System.out.println("Element not found");
return n;
}
// Deleting element
int i;
for (i = pos; i < n - 1; i++)
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
return n - 1;
}
// Driver's Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i;
int arr[] = { 10, 50, 30, 40, 20 };
int n = arr.length;
int key = 30;
System.out.println("Array before deletion");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
// Function call
n = deleteElement(arr, n, key);
System.out.println("\n\nArray after deletion");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
# Python program to delete an element
# from an unsorted array
# Driver's code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Declaring array and key to delete
arr = [10, 50, 30, 40, 20]
key = 30
print("Array before deletion:")
print (arr)
# deletes key if found in the array
# otherwise shows error not in list
arr.remove(key)
print("Array after deletion")
print(arr)
# This code is contributed by Aditi Sharma.
// C# program to implement delete
// operation in an unsorted array
using System;
class main {
// Function to search a
// key to be deleted
static int findElement(int[] arr, int n, int key)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == key)
return i;
return -1;
}
// Function to delete an element
static int deleteElement(int[] arr, int n, int key)
{
// Find position of element
// to be deleted
int pos = findElement(arr, n, key);
if (pos == -1) {
Console.WriteLine("Element not found");
return n;
}
// Deleting element
int i;
for (i = pos; i < n - 1; i++)
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
return n - 1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int i;
int[] arr = { 10, 50, 30, 40, 20 };
int n = arr.Length;
int key = 30;
Console.Write("Array before deletion ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
// Function call
n = deleteElement(arr, n, key);
Console.Write("Array after deletion ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.
// Java script program to implement delete
// operation in an unsorted array
// function to search a key to
// be deleted
function findElement(arr,n,key)
{
let i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == key)
return i;
return -1;
}
// Function to delete an element
function deleteElement(arr,n,key)
{
// Find position of element to be
// deleted
let pos = findElement(arr, n, key);
if (pos == -1)
{
console.log("Element not found");
return n;
}
// Deleting element
let i;
for (i = pos; i< n - 1; i++)
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
return n - 1;
}
// Driver Code
let i;
let arr = [10, 50, 30, 40, 20];
let n = arr.length;
let key = 30;
console.log("Array before deletion<br>");
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
console.log(arr[i] + " ");
n = deleteElement(arr, n, key);
console.log("<br><br>Array after deletion<br>");
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
console.log(arr[i]+" ");
<?php
// PHP program to implement delete
// operation in an unsorted array
// To search a key to be deleted
function findElement(&$arr, $n, $key)
{
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
if ($arr[$i] == $key)
return $i;
return -1;
}
// Function to delete an element
function deleteElement(&$arr, $n, $key)
{
// Find position of element to
// be deleted
$pos = findElement($arr, $n, $key);
if ($pos == -1)
{
echo "Element not found";
return $n;
}
// Deleting element
for ($i = $pos; $i < $n - 1; $i++)
$arr[$i] = $arr[$i + 1];
return $n - 1;
}
// Driver code
$arr = array(10, 50, 30, 40, 20);
$n = count($arr);
$key = 30;
echo "Array before deletion\n";
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
echo $arr[$i] . " ";
// Function call
$n = deleteElement($arr, $n, $key);
echo "\nArray after deletion\n";
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
echo $arr[$i] . " ";
// This code is contributed by
// Rajput-Ji
?>
OutputArray before deletion
10 50 30 40 20
Array after deletion
10 50 40 20
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Similar Reads
Array Data Structure Complete Guide to ArraysLearn more about Array in DSA Self Paced CoursePractice Problems on ArraysTop Quizzes on Arrays What is Array?An array is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations. The idea is to store multiple items of the same type together. This makes it easier to calcul
3 min read
What is Array? Array is a linear data structure where all elements are arranged sequentially. It is a collection of elements of same data type stored at contiguous memory locations. For simplicity, we can think of an array as a flight of stairs where on each step is placed a value (let's say one of your friends).
2 min read
Getting Started with Array Data Structure Array is a collection of items of the same variable type that are stored at contiguous memory locations. It is one of the most popular and simple data structures used in programming. Basic terminologies of ArrayArray Index: In an array, elements are identified by their indexes. Array index starts fr
14 min read
Applications, Advantages and Disadvantages of Array Array is a linear data structure that is a collection of data elements of same types. Arrays are stored in contiguous memory locations. It is a static data structure with a fixed size.Table of ContentApplications of Array Data Structure:Advantages of Array Data Structure:Disadvantages of Array Data
2 min read
Subarrays, Subsequences, and Subsets in Array What is a Subarray?A subarray is a contiguous part of array, i.e., Subarray is an array that is inside another array. In general, for an array of size n, there are n*(n+1)/2 non-empty subarrays. For example, Consider the array [1, 2, 3, 4], There are 10 non-empty sub-arrays. The subarrays are: (1),
10 min read
Basic operations in Array
Searching in ArraySearching is one of the most common operations performed in an array. Array searching can be defined as the operation of finding a particular element or a group of elements in the array. There are several searching algorithms. The most commonly used among them are: Linear Search Binary Search Ternar
4 min read
Array Reverse - Complete TutorialGiven an array arr[], the task is to reverse the array. Reversing an array means rearranging the elements such that the first element becomes the last, the second element becomes second last and so on.Examples: Input: arr[] = {1, 4, 3, 2, 6, 5} Output: {5, 6, 2, 3, 4, 1}Explanation: The first elemen
15+ min read
Rotate an Array by d - Counterclockwise or LeftGiven an array of integers arr[] of size n, the task is to rotate the array elements to the left by d positions.Examples:Input: arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, d = 2Output: {3, 4, 5, 6, 1, 2}Explanation: After first left rotation, arr[] becomes {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1} and after the second rotation, arr[] bec
15+ min read
Print array after it is right rotated K timesGiven an Array of size N and a value K, around which we need to right rotate the array. How do you quickly print the right rotated array?Examples : Input: Array[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}, K = 2.Output: 7 9 1 3 5Explanation:After 1st rotation - {9, 1, 3, 5, 7}After 2nd rotation - {7, 9, 1, 3, 5} Input: Arr
15+ min read
Search, Insert, and Delete in an Unsorted Array | Array OperationsIn this post, a program to search, insert, and delete operations in an unsorted array is discussed.Search Operation:In an unsorted array, the search operation can be performed by linear traversal from the first element to the last element. Coding implementation of the search operation:C++// C++ prog
15+ min read
Search, Insert, and Delete in an Sorted Array | Array OperationsHow to Search in a Sorted Array?In a sorted array, the search operation can be performed by using binary search.Below is the implementation of the above approach:C++// C++ program to implement binary search in sorted array #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int binarySearch(int arr[
15+ min read
Array Sorting - Practice ProblemsSorting an array means arranging the elements of the array in a certain order. Generally sorting in an array is done to arrange the elements in increasing or decreasing order. Problem statement: Given an array of integers arr, the task is to sort the array in ascending order and return it, without u
9 min read
Generating All SubarraysGiven an array arr[], the task is to generate all the possible subarrays of the given array.Examples: Input: arr[] = [1, 2, 3]Output: [ [1], [1, 2], [2], [1, 2, 3], [2, 3], [3] ]Input: arr[] = [1, 2]Output: [ [1], [1, 2], [2] ]Iterative ApproachTo generate a subarray, we need a starting index from t
8 min read
Easy problems on Array
Largest three distinct elements in an arrayGiven an array arr[], the task is to find the top three largest distinct integers present in the array.Note: If there are less than three distinct elements in the array, then return the available distinct numbers in descending order.Examples :Input: arr[] = [10, 4, 3, 50, 23, 90]Output: [90, 50, 23]
6 min read
Second Largest Element in an ArrayGiven an array of positive integers arr[] of size n, the task is to find second largest distinct element in the array.Note: If the second largest element does not exist, return -1. Examples:Input: arr[] = [12, 35, 1, 10, 34, 1]Output: 34Explanation: The largest element of the array is 35 and the sec
14 min read
Move all zeros to end of arrayGiven an array of integers arr[], the task is to move all the zeros to the end of the array while maintaining the relative order of all non-zero elements.Examples: Input: arr[] = [1, 2, 0, 4, 3, 0, 5, 0]Output: arr[] = [1, 2, 4, 3, 5, 0, 0, 0]Explanation: There are three 0s that are moved to the end
15 min read
Rearrange array such that even positioned are greater than oddGiven an array arr[], sort the array according to the following relations: arr[i] >= arr[i - 1], if i is even, ∀ 1 <= i < narr[i] <= arr[i - 1], if i is odd, ∀ 1 <= i < nFind the resultant array.[consider 1-based indexing]Examples: Input: arr[] = [1, 2, 2, 1]Output: [1 2 1 2] Expla
9 min read
Rearrange an array in maximum minimum form using Two Pointer TechniqueGiven a sorted array of positive integers, rearrange the array alternately i.e first element should be a maximum value, at second position minimum value, at third position second max, at fourth position second min, and so on. Examples: Input: arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} Output: arr[] = {7, 1, 6, 2
6 min read
Segregate even and odd numbers using Lomuto’s Partition SchemeGiven an array arr[] of integers, segregate even and odd numbers in the array such that all the even numbers should be present first, and then the odd numbers.Examples: Input: arr[] = {7, 2, 9, 4, 6, 1, 3, 8, 5}Output: 2 4 6 8 7 9 1 3 5Input: arr[] = {1, 3, 2, 4, 7, 6, 9, 10}Output: 2 4 6 10 7 1 9 3
6 min read
Reversal algorithm for Array rotationGiven an array arr[] of size N, the task is to rotate the array by d position to the left. Examples: Input: arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}, d = 2Output: 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2Explanation: If the array is rotated by 1 position to the left, it becomes {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1}.When it is rotated further by 1
15 min read
Print left rotation of array in O(n) time and O(1) spaceGiven an array of size n and multiple values around which we need to left rotate the array. How to quickly print multiple left rotations?Examples : Input : arr[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}k1 = 1k2 = 3k3 = 4k4 = 6Output : 3 5 7 9 17 9 1 3 59 1 3 5 73 5 7 9 1Input : arr[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}k1 = 14 Output : 9 1
15+ min read
Sort an array which contain 1 to n valuesWe are given an array that contains 1 to n elements, our task is to sort this array in an efficient way. We are not allowed to simply copy the numbers from 1 to n.Examples : Input : arr[] = {2, 1, 3};Output : {1, 2, 3}Input : arr[] = {2, 1, 4, 3};Output : {1, 2, 3, 4} Native approach - O(n Log n) Ti
7 min read
Count Possible TrianglesGiven an unsorted array of positive integers, the task is to find the number of triangles that can be formed with three different array elements as three sides of triangles. For a triangle to be possible from 3 values as sides, the sum of the two values (or sides) must always be greater than the thi
15+ min read
Print all Distinct (Unique) Elements in given ArrayGiven an integer array arr[], print all distinct elements from this array. The given array may contain duplicates and the output should contain every element only once.Examples: Input: arr[] = {12, 10, 9, 45, 2, 10, 10, 45}Output: {12, 10, 9, 45, 2}Input: arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}Output: {1, 2, 3, 4,
11 min read
Unique Number IGiven an array of integers, every element in the array appears twice except for one element which appears only once. The task is to identify and return the element that occurs only once.Examples: Input: arr[] = [2, 3, 5, 4, 5, 3, 4]Output: 2 Explanation: Since 2 occurs once, while other numbers occu
8 min read
Leaders in an arrayGiven an array arr[] of size n, the task is to find all the Leaders in the array. An element is a Leader if it is greater than or equal to all the elements to its right side. Note: The rightmost element is always a leader. Examples: Input: arr[] = [16, 17, 4, 3, 5, 2]Output: [17 5 2]Explanation: 17
10 min read
Subarray with Given SumGiven a 1-based indexing array arr[] of non-negative integers and an integer sum. You mainly need to return the left and right indexes(1-based indexing) of that subarray. In case of multiple subarrays, return the subarray indexes which come first on moving from left to right. If no such subarray exi
10 min read
Intermediate problems on Array
Rearrange an array such that arr[i] = iGiven an array of elements of length n, ranging from 0 to n - 1. All elements may not be present in the array. If the element is not present then there will be -1 present in the array. Rearrange the array such that arr[i] = i and if i is not present, display -1 at that place.Examples: Input: arr[] =
13 min read
Alternate Rearrangement of Positives and NegativesAn array contains both positive and negative numbers in random order. Rearrange the array elements so that positive and negative numbers are placed alternatively. A number of positive and negative numbers need not be equal. If there are more positive numbers they appear at the end of the array. If t
11 min read
Reorder an array according to given indexesGiven two integer arrays of the same length, arr[] and index[], the task is to reorder the elements in arr[] such that after reordering, each element from arr[i] moves to the position index[i]. The new arrangement reflects the values being placed at their target indices, as described by index[] arra
15+ min read
Find the smallest missing numberGiven a sorted array of n distinct integers where each integer is in the range from 0 to m-1 and m > n. Find the smallest number that is missing from the array. Examples: Input: {0, 1, 2, 6, 9}, n = 5, m = 10 Output: 3 Input: {4, 5, 10, 11}, n = 4, m = 12 Output: 0 Input: {0, 1, 2, 3}, n = 4, m =
15 min read
Difference Array | Range update query in O(1)You are given an integer array arr[] and a list of queries. Each query is represented as a list of integers where:[1, l, r, x]: Adds x to all elements from arr[l] to arr[r] (inclusive).[2]: Prints the current state of the array.You need to perform the queries in order.Examples : Input: arr[] = [10,
10 min read
Stock Buy and Sell – Max 2 Transactions AllowedIn the stock market, a person buys a stock and sells it on some future date. Given the stock prices of n days in an array prices[ ]. Find out the maximum profit a person can make in at most 2 transactions. A transaction is equivalent to (buying + selling) of a stock and a new transaction can start o
15+ min read
Smallest subarray with sum greater than a given valueGiven an array arr[] of integers and a number x, the task is to find the smallest subarray with a sum strictly greater than x.Examples:Input: x = 51, arr[] = [1, 4, 45, 6, 0, 19]Output: 3Explanation: Minimum length subarray is [4, 45, 6]Input: x = 100, arr[] = [1, 10, 5, 2, 7]Output: 0Explanation: N
15+ min read
Count Inversions of an ArrayGiven an integer array arr[] of size n, find the inversion count in the array. Two array elements arr[i] and arr[j] form an inversion if arr[i] > arr[j] and i < j.Note: Inversion Count for an array indicates that how far (or close) the array is from being sorted. If the array is already sorted
15+ min read
Merge Two Sorted Arrays Without Extra SpaceGiven two sorted arrays a[] and b[] of size n and m respectively, the task is to merge both the arrays and rearrange the elements such that the smallest n elements are in a[] and the remaining m elements are in b[]. All elements in a[] and b[] should be in sorted order.Examples: Input: a[] = [2, 4,
15+ min read
Majority ElementYou are given an array arr, and your task is to find the majority element an element that occurs more than half the length of the array (i.e., arr.size() / 2). If such an element exists return it, otherwise return -1, indicating that no majority element is present.Examples : Input : arr[] = [1, 1, 2
15+ min read
Two Pointers TechniqueTwo pointers is really an easy and effective technique that is typically used for Two Sum in Sorted Arrays, Closest Two Sum, Three Sum, Four Sum, Trapping Rain Water and many other popular interview questions. Given a sorted array arr (sorted in ascending order) and a target, find if there exists an
11 min read
3 Sum - Triplet Sum in ArrayGiven an array arr[] of size n and an integer sum, the task is to check if there is a triplet in the array which sums up to the given target sum.Examples: Input: arr[] = [1, 4, 45, 6, 10, 8], target = 13Output: true Explanation: The triplet [1, 4, 8] sums up to 13Input: arr[] = [1, 2, 4, 3, 6, 7], t
15 min read
Equilibrium IndexGiven an array arr[] of size n, the task is to return an equilibrium index (if any) or -1 if no equilibrium index exists. The equilibrium index of an array is an index such that the sum of all elements at lower indexes equals the sum of all elements at higher indexes. Note: When the index is at the
15 min read
Hard problems on Array
MO's Algorithm (Query Square Root Decomposition) | Set 1 (Introduction)Let us consider the following problem to understand MO's Algorithm. We are given an array and a set of query ranges, we are required to find the sum of every query range.Example: Input: arr[] = {1, 1, 2, 1, 3, 4, 5, 2, 8}; query[] = [0, 4], [1, 3] [2, 4]Output: Sum of arr[] elements in range [0, 4]
15+ min read
Square Root (Sqrt) Decomposition AlgorithmSquare Root Decomposition Technique is one of the most common query optimization techniques used by competitive programmers. This technique helps us to reduce Time Complexity by a factor of sqrt(N) The key concept of this technique is to decompose a given array into small chunks specifically of size
15+ min read
Sparse TableSparse table concept is used for fast queries on a set of static data (elements do not change). It does preprocessing so that the queries can be answered efficiently.Range Minimum Query Using Sparse TableYou are given an integer array arr of length n and an integer q denoting the number of queries.
15+ min read
Range sum query using Sparse TableWe have an array arr[]. We need to find the sum of all the elements in the range L and R where 0 <= L <= R <= n-1. Consider a situation when there are many range queries. Examples: Input : 3 7 2 5 8 9 query(0, 5) query(3, 5) query(2, 4) Output : 34 22 15Note : array is 0 based indexed and q
8 min read
Range LCM QueriesGiven an array arr[] of integers of size N and an array of Q queries, query[], where each query is of type [L, R] denoting the range from index L to index R, the task is to find the LCM of all the numbers of the range for all the queries.Examples: Input: arr[] = {5, 7, 5, 2, 10, 12 ,11, 17, 14, 1, 4
15+ min read
Jump Game - Minimum Jumps to Reach EndGiven an array arr[] of non-negative numbers. Each number tells you the maximum number of steps you can jump forward from that position.For example:If arr[i] = 3, you can jump to index i + 1, i + 2, or i + 3 from position i.If arr[i] = 0, you cannot jump forward from that position.Your task is to fi
15+ min read
Space optimization using bit manipulationsThere are many situations where we use integer values as index in array to see presence or absence, we can use bit manipulations to optimize space in such problems.Let us consider below problem as an example.Given two numbers say a and b, mark the multiples of 2 and 5 between a and b using less than
12 min read
Maximum value of Sum(i*arr[i]) with array rotations allowedGiven an array arr[], the task is to determine the maximum possible value of the expression i*arr[i] after rotating the array any number of times (including zero).Note: In each rotation, every element of the array shifts one position to the right, and the last element moves to the front.Examples : I
12 min read
Construct an array from its pair-sum arrayGiven a pair-sum array construct the original array. A pair-sum array for an array is the array that contains sum of all pairs in ordered form, i.e., pair[0] is sum of arr[0] and arr[1], pair[1] is sum of arr[0] and arr[2] and so on. Note that if the size of input array is n, then the size of pair a
5 min read
Maximum equilibrium sum in an arrayGiven an array arr[]. Find the maximum value of prefix sum which is also suffix sum for index i in arr[].Examples : Input : arr[] = {-1, 2, 3, 0, 3, 2, -1}Output : 4Explanation : Prefix sum of arr[0..3] = Suffix sum of arr[3..6]Input : arr[] = {-3, 5, 3, 1, 2, 6, -4, 2}Output : 7Explanation : Prefix
11 min read
Smallest Difference Triplet from Three arraysThree arrays of same size are given. Find a triplet such that maximum - minimum in that triplet is minimum of all the triplets. A triplet should be selected in a way such that it should have one number from each of the three given arrays. If there are 2 or more smallest difference triplets, then the
9 min read
Top 50 Array Coding Problems for Interviews Array is one of the most widely used data structure and is frequently asked in coding interviews to the problem solving skills. The following list of 50 array coding problems covers a range of difficulty levels, from easy to hard, to help candidates prepare for interviews.Easy ProblemsSecond Largest
2 min read