Spring Boot - Eureka Server
Last Updated :
04 Jan, 2025
In modern microservices architectures, service registration and discovery are crucial components that enable seamless communication between different services. Netflix's Eureka Server, integrated with Spring Boot, provides an elegant solution for managing these aspects. In this article, we will dive into the configuration and usage of Eureka Server, understanding why it's essential, exploring its benefits, and considering alternatives.
Why use Eureka Server?
Eureka Server is a service registry that plays a central role in the automatic detection of devices and services on a network. It acts as the heart of your microservices ecosystem, allowing service instances to register themselves and facilitating service discovery. Key aspects of Eureka Server include:
- Client Registration: Instances of microservices automatically register themselves with Eureka Server.
- Service Discovery: Eureka Server maintains a registry of all client applications running on different ports and IP addresses.
Benefits of using Eureka Server in Spring Boot Applications
Eureka Server operates on a simple "Register, Lookup, Connect" principle, making it an excellent choice for managing microservices in a Spring Boot environment. Here are some compelling reasons to use Eureka Server:
- Centralized Service Registry: Eureka Server knows about all client applications and their locations. This centralization simplifies service discovery.
- Automatic Registration: Microservices automatically register themselves with Eureka Server, reducing manual configuration efforts.
- Load Balancing: Eureka Server can help implement load balancing among service instances.
- Health Checks: Eureka Server can perform health checks on registered services, ensuring robustness and reliability.
- Integration with Spring Cloud: Eureka Server seamlessly integrates with the Spring Cloud ecosystem, enabling easy scaling and deployment.
Use cases of Eureka Server
Eureka Server finds applications in various scenarios, including:
- Microservices Architecture: Eureka is a fundamental building block for microservices-based applications.
- Distributed Systems: It simplifies the management of service discovery in complex, distributed systems.
- Load Balancing: Eureka can be used in conjunction with load balancers to distribute traffic evenly among service instances.
1. Configuring the Eureka Server
1.1 POM config
You need to do the below configuration into your project's pom.xml on server and client side, to get automatic registration and uninterrupted connection of client to server.
XML
<!-- For Eureka Client -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- For Eureka Server -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
Note: Ensure that you also have spring-cloud-dependencies defined in your pom.xml below given dependencyManegement in case you are manually importing.
XML
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2021.0.5</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
1.2 Bean Configuration
No bean configuration is required for simple use cases. You'll mostly use annotations to enable Eureka functionality:
- @EnableEurekaServer: Use this annotation to designate a Spring Boot application as the central instance where other services will get registered.
- @EnableEurekaClient: Services use this annotation to enable service registration and discovery with the central Eureka Server.
1.3 Application Properties
Your application.properties or application.yml file should contain Eureka-related configuration. For example:
eureka:
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
client:
fetch-registry: true
register-with-eureka: true
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka
Note: To identify and locate other microservices with application name "spring.application.name=TEACHER-APP"
This configuration ensures that the Eureka client instances prefer using IP addresses, fetch the registry, and register themselves with the Eureka Server running on the default "http://localhost:8761"
Implementing Eureka Configuration
For marking a Spring Boot Application as an Eureka Server
Java
package org.geeksforgeeks.registry.ServiceRegistry;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class ServiceRegistryApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ServiceRegistryApplication.class, args);
}
}
For marking a Spring Boot Application as an Eureka Client to be used up by the server
Java
package org.geeksforgeeks.student;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
public class StudentApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StudentApplication.class, args);
}
}
Eureka Dashboard
When your Spring Boot application is up and running. Hit the default URL - http://localhost:8761. It shows that Eureka has discovered 3 microservices up and running on the device, that are:
- API-GATEWAY
- STUDENT-APP
- TEACHER-APP
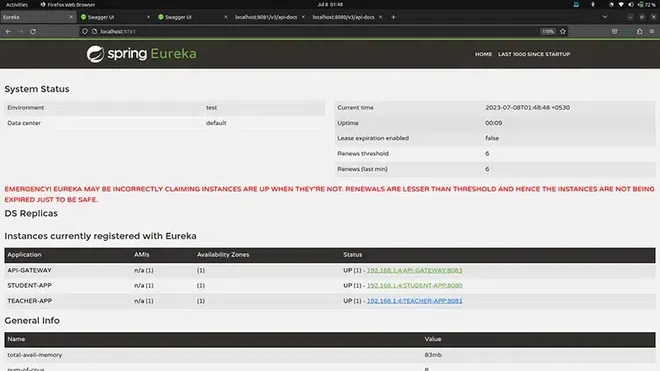 Dashboard of Eureka discovery client
Dashboard of Eureka discovery client
Alternatives to Eureka Client
Eureka is the most popular choice for service registration and discovery, but we do have some alternatives such as Consul and ZooKeeper that provide similar capabilities and may be found more useful for specific use cases. You can also refer to docs for integration-related issues.
Conclusion
We have been through the service registration and discovery of services with Eureka Server in your Spring Boot Application. By adding the Eureka Server dependency, configuring application properties, and use case for Eureka Annotations.
Similar Reads
Spring Boot - Servlet Filter
Spring boot Servlet Filter is a component used to intercept & manipulate HTTP requests and responses. Servlet filters help in performing pre-processing & post-processing tasks such as: Logging and Auditing: Logging operations can be performed by the servlet filter logging the request and res
8 min read
Spring Boot - Admin Server
Spring boot is one of the most popular applications to develop Java enterprise applications. When you have so many components in your application, you need to monitor and manage them. You have multiple spring boot applications running you need an admin for monitoring. Spring boot admin provides you
4 min read
Spring Boot - REST Example
In modern web development, most applications follow the Client-Server Architecture. The Client (frontend) interacts with the server (backend) to fetch or save data. This communication happens using the HTTP protocol. On the server, we expose a bunch of services that are accessible via the HTTP proto
4 min read
Spring Boot Kafka Producer Example
Spring Boot is one of the most popular and most used frameworks of Java Programming Language. It is a microservice-based framework and to make a production-ready application using Spring Boot takes very less time. Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based Applica
3 min read
Spring Boot Ecosystem
The Spring Framework is one of the most popular frameworks for developing stand-alone Java applications. Spring Boot is a part of the Spring Framework. Spring boot supports rapid application development by automating various manual configurations needed for traditional Spring MVC architecture. Sprin
4 min read
Spring Cloud - Securing Services
Spring Cloud Security is an extremely versatile and strong framework for access control and authentication. To secure the Spring-based applications, this is a good mechanism. A Java application's authentication and authorization are the main goals of the Spring Security framework. Our application ca
5 min read
Server - Sent Events in Spring
When we design web applications, we generally have a client and a server model, where the client is always the initiator of the transaction or a request to the server. The server responds to these requests. However, in certain scenarios, there arises a need for the server to respond much more freque
5 min read
Spring Boot Without A Web Server
Spring Boot is a widely used framework used for building Java applications. It comes with lots of features that make a developer's life easy. Out of those features, spring boot applications come with an embedded server in it. The default server being used in spring boot applications is Apache Tomcat
3 min read
Spring Boot - @Requestmapping
Spring Boot is the most popular framework of Java for building enterprise-level web applications and back-ends. Spring Boot has a handful of features that support quicker and more efficient web app development. Some of them are Auto-configuration, Embedded Server, opinionated defaults, and Annotatio
6 min read
Debugging Eureka Issues in Spring Boot Microservices
Debugging Eureka issues in Spring Boot microservices involves several steps and checks to ensure proper registration, discovery, and communication between services. Debugging the Eureka issues can typically involve checking the following: Eureka Server and Client Configurations.Network connectivity
4 min read