Exception handling in Spring MVC allows developers to handle runtime errors gracefully and return meaningful responses instead of application crashes. It helps in building robust, user-friendly, and maintainable web applications.
- Prevents application failure due to unhandled runtime exceptions
- Provides centralized and reusable error-handling mechanisms
Types of Exception Handling in Spring MVC
Spring MVC supports the following approaches:
1. Try–Catch Block
Try–catch is the most basic way of handling exceptions directly inside controller methods.
@RequestMapping("/welcome")
public String processForm(@ModelAttribute Student student, Model model) {
try {
int roll = Integer.parseInt(student.getRollNo());
model.addAttribute("roll", roll);
return "welcome";
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
model.addAttribute("err", "Invalid Roll Number");
return "error";
}
}
Key points:
- Simple and easy to understand
- Handles exceptions locally within the method
- Not suitable for large applications
2. @ExceptionHandler
@ExceptionHandler handles specific exceptions at the controller level.
@ExceptionHandler(NumberFormatException.class)
public String handleNumberFormat(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("err", "Number Format Exception");
return "error";
}
Drawbacks:
- Cleaner than try–catch
- Handles exceptions for a single controller
- Improves code readability
- Limited to one controller
3. @ControllerAdvice
@ControllerAdvice provides global exception handling across all controllers.
Example:
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(NullPointerException.class)
public String handleNull(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("err", "Null Pointer Exception");
return "error";
}
}
Key points:
- Centralized error handling
- Applies to all controllers
- Reduces duplicate code
- Less control over individual controllers
4. @ResponseStatus
@ResponseStatus maps exceptions directly to HTTP status codes.
Example:
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class ResourceNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
}
Key Points:
- Simple mapping to HTTP status
- No extra handler methods required
- Useful for REST APIs
- Not suitable for complex error responses
5. HandlerExceptionResolver
HandlerExceptionResolver is a low-level interface for custom exception resolution.
Example:
public class MyExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
public ModelAndView resolveException(
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler,
Exception ex) {
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView("error");
mv.addObject("err", ex.getMessage());
return mv;
}
}
Key Points:
- Full control over exception handling
- Works before controller execution ends
- Highly customizable
- More complex to implement
6. Spring Boot Default Exception Handling
Spring Boot provides built-in exception handling via BasicErrorController.
Example: No custom code required-Spring Boot automatically returns error responses like:-
{
"status": 404,
"error": "Not Found",
"path": "/invalid-url"
}
Key Points:
- Enabled by default
- Auto-configured error responses
- Best for quick REST applications
- Not suitable for custom UI error pages
Steps to Create the Application
Step 1: Create a Maven Web Application
- Open Eclipse IDE
- Create a New Maven Project
- Select maven-archetype-webapp
- Enter Group Id and Artifact Id
- Click Finish
After project creation, the basic project structure is generated automatically.

After clicking finish your project structure would look something like this:

Step 2: Project Structure
After adding all the classes and configuration files your project would look something like this:

Step 3: Configure pom.xml
The pom.xml is auto-created with any maven project, it defines all the dependencies required for the project. Make sure to add all the dependencies mentioned in this file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.gfg</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringMvcExceptionHandling</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>SpringMvcExceptionHandling Maven Webapp</name>
<!-- FIXME change it to the project's website -->
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-jasper</artifactId>
<version>9.0.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.0-alpha-1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>SpringMvcExceptionHandling</finalName>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.22.1</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
</project>
Step 4: Configure web.xml
The web.xml file maps incoming requests to the DispatcherServlet, which is the front controller of Spring MVC.
<web-app xmlns="http://www.oracle.com/webfolder/technetwork/jsc/xml/ns/javaee/index.html"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.oracle.com/webfolder/technetwork/jsc/xml/ns/javaee/index.html
http://www.oracle.com/webfolder/technetwork/jsc/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"
version="3.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>gfg</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/gfg-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>gfg</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Step 5: Configure Spring MVC (gfg-servlet.xml)
This file enables:
- Component scanning
- Annotation-driven MVC
- View resolution for JSP files
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans//spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc//spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/ \
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context//spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.gfg" />
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix">
<value>/WEB-INF/views/</value>
</property>
<property name="suffix">
<value>.jsp</value>
</property>
</bean>
<mvc:annotation-driven />
</beans>
Step 6: Create the Model Class (Student)
The rollNo field is intentionally kept as String to demonstrate a NumberFormatException.
package com.gfg.model;
public class Student {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String rollNo;
public Student(String firstName, String lastName,
String rollNo)
{
super();
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
public Student() {}
public String getFirstName() { return firstName; }
public void setFirstName(String firstName)
{
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() { return lastName; }
public void setLastName(String lastName)
{
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getRollNo() { return rollNo; }
public void setRollNo(String rollNo)
{
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
}
Step 7:Create Controller with Method-Level Exception Handling
- The LoginController has two methods: showForm (GET) to display the login form, and processForm to handle form data using @ModelAttribute and Model.
- The rollNo field in the Student class is a String but parsed to int, which may throw a NumberFormatException if it's empty or contains letters.
- To handle this, a method numberformatHandler is defined with @ExceptionHandler(NumberFormatException.class) to catch the error and improve user experience.
package com.gfg.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import com.gfg.model.Student;
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String showForm(Model theModel) {
theModel.addAttribute("student", new Student());
return "portal";
}
@RequestMapping("/welcome")
public String processForm(@ModelAttribute("welcome") Student student, Model mod) {
mod.addAttribute("FirstName", student.getFirstName());
mod.addAttribute("LastName", student.getLastName());
int n = Integer.parseInt(student.getRollNo());
mod.addAttribute("RollNo", n);
return "welcome";
}
@ExceptionHandler(value = NumberFormatException.class)
public String numberformatHandler(Model theModel) {
theModel.addAttribute("err", "NumberFormatException");
return "error";
}
}
Step 8: Global Exception Handling Using @ControllerAdvice
- The MyExceptionHandler class handles all exceptions in the app and shows user-friendly error pages.
- By adding @ControllerAdvice, it applies to all controllers, allowing Spring MVC to use custom error methods instead of server-generated pages. This is an example of class-level exception handling.
package com.gfg.errorhandler;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = NullPointerException.class)
public String nullPointerHandler(Model theModel) {
theModel.addAttribute("err", "NullPointerException");
return "error";
}
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public String AnyOtherHandler() {
return "error";
}
}
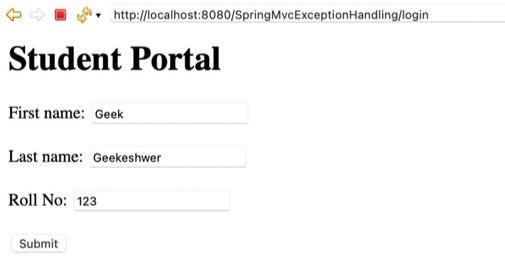
Step 9: Create JSP Views
This file in the views folder defines the Student login portal.
portal.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="form" url="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Student Portal</h1>
<form:form action="welcome" modelAttribute="student">
<label>First name:</label>
<form:input path="firstName" />
<br><br>
<label>Last name:</label>
<form:input path="lastName" />
<br><br>
<label>Roll No:</label>
<form:input path="rollNo" />
<br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
welcome.jsp:
This page in the views folder defines the welcome page for our application.
<%@ taglib prefix="form" url="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Student Portal</h1>
<form:form action="welcome" modelAttribute="student">
<label>First name:</label>
<form:input path="firstName" />
<br><br>
<label>Last name:</label>
<form:input path="lastName" />
<br><br>
<label>Roll No:</label>
<form:input path="rollNo" />
<br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
error.jsp
This page is a simple exception handler page that defines the name of the exception and informs the user about an exception.
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Opps....</h1>
<h1> ${err} Exception caused</h1>
</body>
</html>
Step 10: Run the Application
Deploy the application on Apache Tomcat and access:
http://localhost:8080/SpringMvcExceptionHandling/login
Enter invalid roll number data to trigger exceptions.
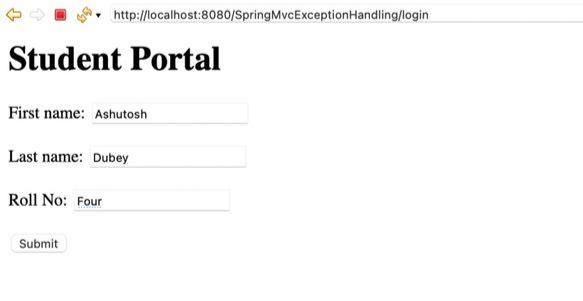
When Roll No is invalid:

Fill Correct data: