Spring @ResponseBody Annotation with Example
Last Updated :
12 Apr, 2025
Spring Annotations allow us to configure dependencies and implement dependency injection through java programs. Those are used to provide supplemental information about a program. It does not have a direct effect on the operation of the code they annotate. It does not change the action of the compiled program. The @ResponseBody annotation tells a controller that the object returned is automatically serialized into JSON and passed back into the HttpResponse object. When you use the @ResponseBody annotation on a method, Spring converts the return value and writes it to the HTTP response automatically. Each method in the Controller class must be annotated with @ResponseBody.

So let's understand @ResponseBody Annotation by an example.
Implementation:
Requirements:
Setting Up the Project
Note: We are going to use Spring Tool Suite 4 IDE for this project. Please refer to this article to install STS in your local machine How to Download and Install Spring Tool Suite (Spring Tools 4 for Eclipse) IDE?
Step 1: Create a Dynamic Web Project in your STS IDE. You may refer to this article to create a Dynamic Web Project in STS: How to Create a Dynamic Web Project in Spring Tool Suite?
Step 2: Download the spring JARs file and go to the src > main > webapp > WEB-INF > lib folder and past these JAR files.
Step 3: Configure the tomcat server with your application. Now we are ready to go.
it is recommended to refer to article: Configuration of Apache Tomcat Server
Configuring Dispatcher Servlet
Tip: Please refer to this article What is Dispatcher Servlet in Spring? and read more about Dispatcher Servlet which is a very very important concept to understand. Now we are going to configure Dispatcher Servlet with our Spring MVC application.
Step 4: Go to the src > main > webapp > WEB-INF > web.xml file and the complete code for web.xml file is given below:
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="4.0">
<display-name>myfirst-mvc-project</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<absolute-ordering/>
<servlet>
<!-- Provide a Servlet Name -->
<servlet-name>frontcontroller-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<!-- Provide a fully qualified path to the DispatcherServlet class -->
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<!-- Provide a Servlet Name that you want to map -->
<servlet-name>frontcontroller-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<!-- Provide a url pattern -->
<url-pattern>/student.com/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Step 5: Now go to the src > main > webapp > WEB-INF and create an XML file. Actually, this is a Spring Configuration file like beans.xml file. And the name of the file must be in this format:
YourServletName-servlet.xml
For example, for this project, the name of the file must be
frontcontroller-dispatcher-servlet.xml
So either you can create a Spring Configuration File or you can just create a simple XML file add the below lines of code inside that file.
FIle: frontcontroller-dispatcher-servlet.xml
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.student.controllers"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
Creating Controller Class
Step 6: Now, let's create some controllers. Go to the src/main/java and create a new controllers package (For ex. com.student.controllers) as per your choice. And inside that create a Java class and name the class as DemoController. Now how to tell the Spring that this is our controller class. So the way we are going to tell the Spring is by marking it with a @Controller annotation.
@Controller
public class DemoController
{
}
Note: Spring will automatically initialize the class having a @Controller annotation and register that class with the spring container.
Now let us create a simple method inside the Controller class and use @ResponseBody annotation before the method something like this.
// Annotation
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/hello")
// Method
public String helloWorld()
{
return "Hello World!";
}
Now let's understand the annotation. So basically @RequestMapping("/hello"), this line means, in the URL if somebody hits student.com/hello then this particular method will be executed and it is going to perform the operation that is written inside that particular method. For example, for this project, we are just returning a message "Hello World!" and we are expecting this is going to display in the client browser. But this thing will not happen. And to make it happen we need to use the @ResponseBody annotation. So @ResponseBody annotation is basically gonna write this particular message, here "Hello World!", in your HTTP response.
File: DemoController.java
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate DemoController Class
package com.student.controllers;
// Importing required classes
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
// Annotation
@Controller
// Class
public class DemoController {
// Annotation
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/hello")
// Method
public String helloWorld()
{
return "Hello World!";
}
}
Running Spring MVC Controller
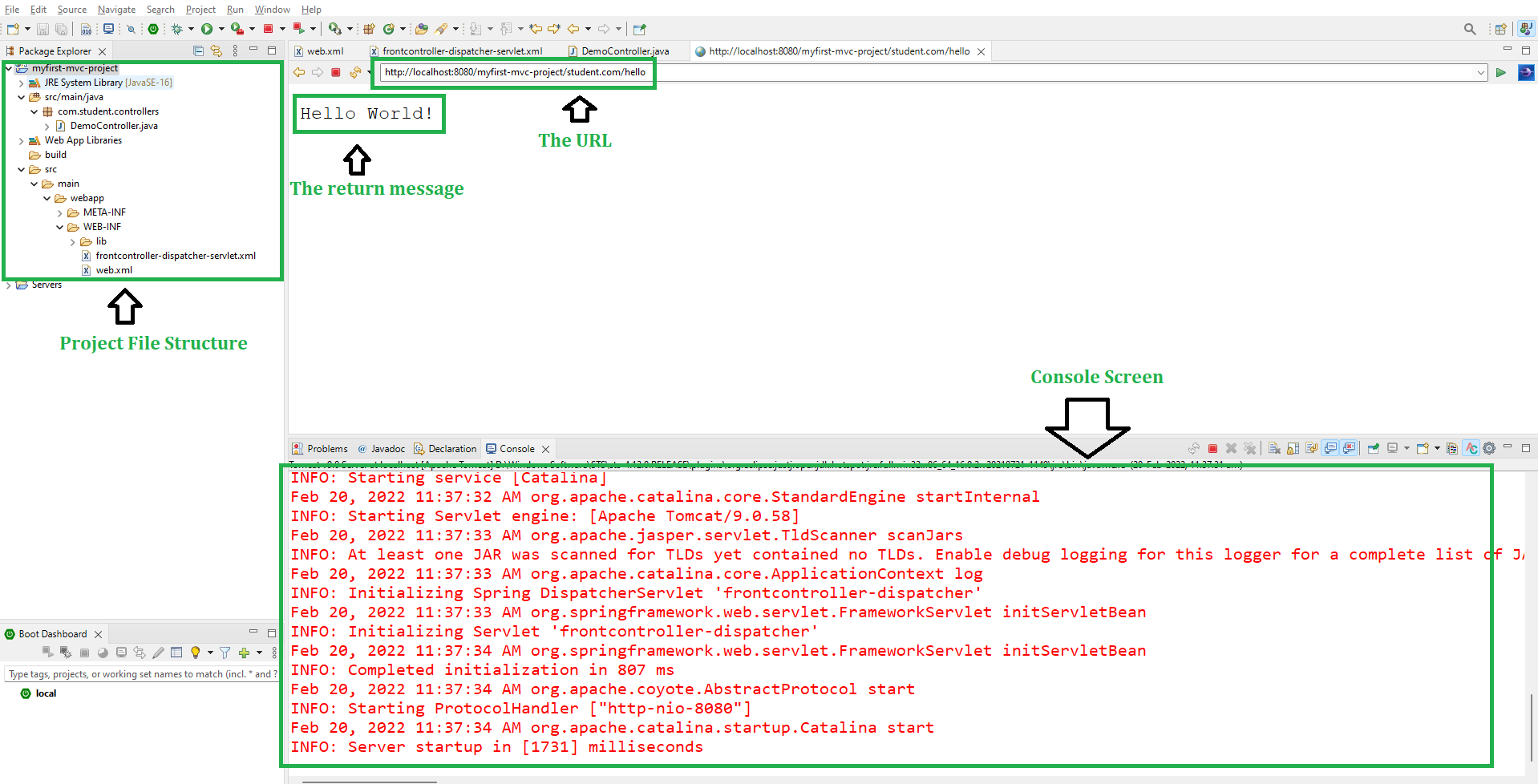
Step 7: To run your Spring MVC Application right-click on your project > Run As > Run on Server and run your application. After that use the following URL to run your controller as shown in the below image. All other details are mentioned in the image.
http://localhost:8080/myfirst-mvc-project/student.com/hello
Similar Reads
Spring MVC - Multiple View Page A view page is redirected to another view page in this example. Let's look at a simple Spring Web MVC framework sample. The procedure is as follows: In the case of Maven, load the spring jar files or add dependencies.Make your controller class.Provide a controller entry in the web.xml file.In a sepa
3 min read
Spring MVC - Custom Validation Validating user input is essential for any web application to ensure the processing of valid data. The Spring MVC framework supports the use of validation API. The validation API puts constraints on the user input using annotations and can validate both client-side and server-side. It provides stand
8 min read
Difference Between ApplicationContext and WebApplicationContext in Spring MVC Spring MVC framework enables separation of modules namely Model, View, and Controller, and seamlessly handles the application integration. This enables the developer to create complex applications also using plain Java Classes. The model object can be passed between view and controller using maps. W
3 min read
Difference Between @Component, @Repository, @Service, and @Controller Annotations in Spring Spring Annotations are a form of metadata that provides data about a program. Annotations are used to provide supplemental information about a program. It does not have a direct effect on the operation of the code they annotate. It does not change the action of the compiled program. Here, we are goi
4 min read
Difference Between @Controller and @Service Annotation in Spring Spring Annotations are a form of metadata that provides data about a program. Annotations are used to provide supplemental information about a program. It does not have a direct effect on the operation of the code they annotate. It does not change the action of the compiled program. Spring @Control
5 min read
Difference Between @Controller and @RestController Annotation in Spring Spring Annotations are a form of metadata that provides data about a program. Annotations are used to provide supplemental information about a program. It does not directly affect the operation of the code they annotate. It does not change the action of the compiled program. Understanding the differ
3 min read
Spring MVC - @RequestParam Annotation The @RequestParam annotation is one of the most commonly used annotations in Spring MVC for handling HTTP request parameters. @RequestParam annotation enables Spring to extract input data that may be passed as a query, form data, or any arbitrary custom data. Key features of @RequestParam annotation
5 min read
Query String and Query Parameter in Spring MVC According to Wikipedia "A query string is a part of a uniform resource locator (URL) that assigns values to specified parameters. A query string commonly includes fields added to a base URL by a Web browser or other client application, for example as part of an HTML, choosing the appearance of a pag
6 min read
How to Make Post Request in Java Spring? Java language is one of the most popular languages among all programming languages. There are several advantages of using the java programming language, whether for security purposes or building large distribution projects. One of the advantages of using JAVA is that Java tries to connect every conc
4 min read
How to Make Delete Request in Spring? Java language is one of the most popular languages among all programming languages. There are several advantages of using the java programming language, whether for security purposes or building large distribution projects. One of the advantages of using JAVA is that Java tries to connect every conc
4 min read