How to Make a Simple RestController in Spring Boot?
Last Updated :
03 Sep, 2025
A RestController in Spring Boot is a specialized controller that is used to develop RESTful web services. It is marked with the @RestController annotation, which combines @Controller and @ResponseBody. This ensures that the response is automatically converted into JSON or XML, eliminating the need for explicit response conversions.
Steps to Create a Simple RestController in Spring Boot
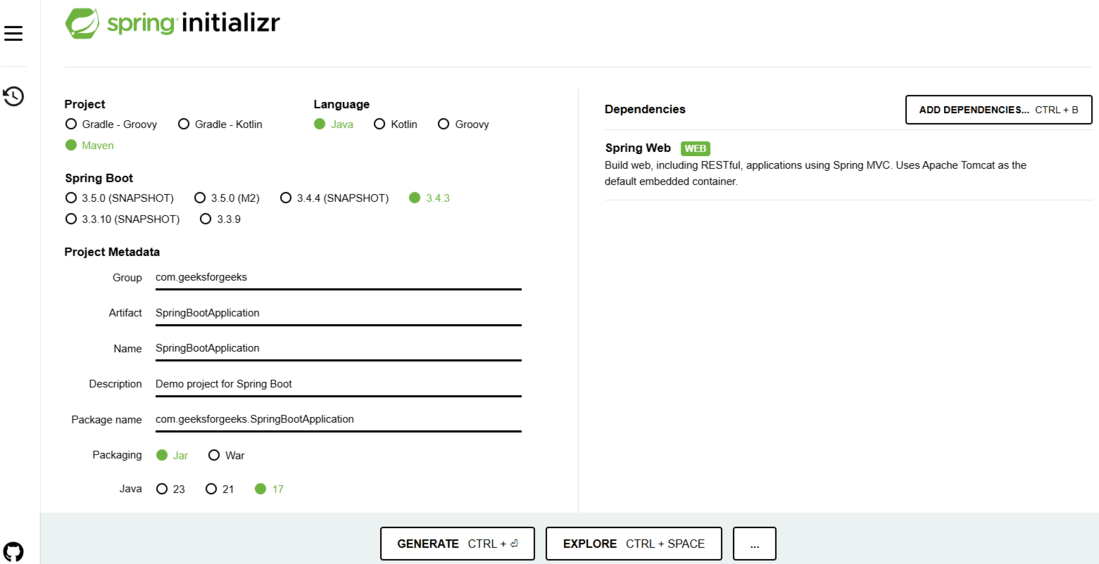
Step 1: Setup Spring Boot Project Using Spring Initializr
1. Go to Spring Initializr.
2. Configure the project with the following details:
- Project: Maven
- Language: Java
- Spring Boot Version: 3.x (Latest Version)
- Packaging: JAR
- Java Version: 17 or later
- Dependencies: Spring Web
Click on Generate to download the project.
 project
projectStep 2: Import the Project into Your IDE
Extract the zip file. Now open a suitable IDE and then go to File > New > Project from existing sources and select pom.xml. Click on import changes on prompt and wait for dependencies to load.

Note:
In the Import Project for Maven window, make sure you choose the same version of JDK which you selected while creating the project.
Step 3: Create a Simple RestController
Go to src -> main -> java -> com.geeksforgeeks.SpringBootApplication, create a new Java class with the name Controller.java and add the annotation @RestController.
Controller.java:
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.SpringBootApplication.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class Controller {
@GetMapping("/hello/{name}/{age}")
public String sayHello(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable int age) {
return "Hello, " + name + "! You are " + age + " years old.";
}
}
Explanation:
- @RestController annotation marks this class as a RESTful controller.
- @RequestMapping("/api") defines a base URL for all endpoints inside this controller.
- @GetMapping("/hello/{name}/{age}") handles HTTP GET requests and extracts name and age from the URL.
- @PathVariable annotation captures dynamic values from the request URL.
- Returns a simple JSON response with a greeting message.
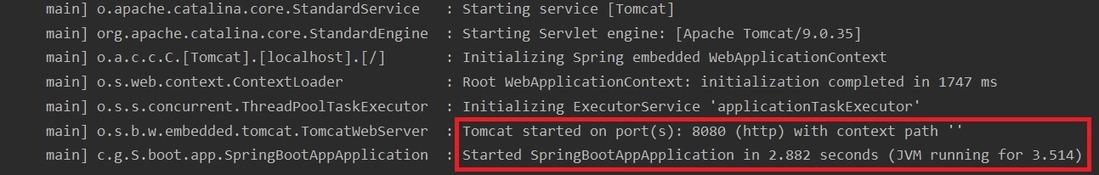
Step 4: Run the Spring Boot Application
Run the main class and wait for the Tomcat server to start.
Note:
The default port of the Tomcat server is 8080 and can be changed in the application.properties file.
This Controller.java file is used for handling all incoming requests from the client-side.
Step 5: Test the API
Once the application starts, test the API by opening a browser or using Postman:
http://localhost:8080/api/hello/Sweta/25
Response:
"Hello, Sweta! You are 25 years old."
Explore
Spring Boot Basics and Prerequisites
Spring Boot Core
Spring Boot with REST API
Spring Boot with Database and Data JPA
Spring Boot with Kafka
Spring Boot with AOP