Spring - ResultSetExtractor
Last Updated :
08 Oct, 2025
ResultSetExtractor is an interface used to extract data from a ResultSet object returned by executing an SQL query. It is especially useful when mapping an entire ResultSet (multiple rows or nested data) into a single object or collection.
- Used when a RowMapper is not sufficient (e.g., custom or hierarchical mapping).
- Allows manual control over ResultSet iteration and transformation.
- The JdbcTemplate.query() method accepts a ResultSetExtractor instance.
Method Syntax:
Java
public T extractData(ResultSet resultSet) throws SQLException, DataAccessException;
query() method syntax:
Java
public <T> T query(String sql, ResultSetExtractor<T> resultSetExtractor);
- Java: 21 or later
- Spring Boot: Version 3.2.0 or higher
- Database: MySQL
- Build Tool: Maven
Step-by-Step Implementation
Step 1: Define the Database Schema
Execute the following SQL statements to create and populate the Student table.
CREATE TABLE Student (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
department VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO Student (name, department)
VALUES ('geek', 'computer science');
Step 2: Add Dependencies
Include the following dependencies in your pom.xml file.
pom.xml:
XML
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>resultset-extractor-demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<properties>
<java.version>21</java.version>
<spring-boot.version>3.2.0</spring-boot.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Starter JDBC -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL Connector -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<version>8.0.33</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Boot Starter Test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Step 3: Create a Model Class
Define the model class representing the student entity.
Student.java:
Java
public record Student(int id, String name, String department) {}
Step 4: Create a DAO Interface
Create a StudentDao interface for database access operations.
Java
import java.util.List;
public interface StudentDao {
List<Student> getAllStudents();
}
Create the implementation class that uses ResultSetExtractor to map query results.
StudentDaoImpl.java:
Java
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.ResultSetExtractor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Repository
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao {
private final JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public StudentDaoImpl(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
@Override
public List<Student> getAllStudents() {
String sql = "SELECT id, name, department FROM Student";
return jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new StudentResultSetExtractor());
}
private static class StudentResultSetExtractor implements ResultSetExtractor<List<Student>> {
@Override
public List<Student> extractData(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
while (rs.next()) {
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
String department = rs.getString("department");
students.add(new Student(id, name, department));
}
return students;
}
}
}
Add the configuration to application.yml.
application.yml:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school_db
username: root
password: pass
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
Step 7: Create the Main Application Class
Create a main class to bootstrap the Spring Boot application.
ResultSetExtractorApplication.java:
Java
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ResultSetExtractorApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ResultSetExtractorApplication.class, args);
}
}
Step 8: Write the Test Class
Write a simple integration test to verify data fetching.
StudentDaoTest.java:
Java
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.List;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertFalse;
@SpringBootTest
public class StudentDaoTest {
@Autowired
private StudentDao studentDao;
@Test
public void testGetAllStudents() {
List<Student> students = studentDao.getAllStudents();
assertFalse(students.isEmpty());
students.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
Step 9: Run the Application
Run the project using:
mvn spring-boot:run
Output
When executed, the console will print the student records retrieved from the database.
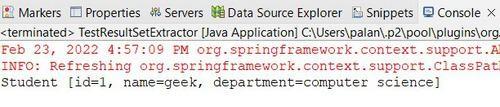 Output
Output
Explore
Spring Boot Basics and Prerequisites
Spring Boot Core
Spring Boot with REST API
Spring Boot with Database and Data JPA
Spring Boot with Kafka
Spring Boot with AOP