Index Optimization in SQL refers to creating and managing indexes on database tables to speed up data retrieval. An index works like the index of a book; instead of searching every page (full table scan), the database can quickly jump to the exact location where the data is stored.
Proper index optimization reduces query execution time and improves overall performance, especially on large tables.
Let's understand this with the help of example
Suppose we have an employees table:
CREATE TABLE employees (
emp_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
emp_name VARCHAR(50),
department VARCHAR(30),
salary DECIMAL(10,2)
);
How to Create an Index
Create an index by defining key columns to optimize data retrieval.
CREATE INDEX idx_department ON employees(department);
Let's execute the query
SELECT emp_name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE department = 'IT';
Output:
EMP_NAME | SALARY |
|---|
RAHUL | 50000 |
|---|
PRIYA | 60000 |
|---|
AMIT | 55000 |
|---|
Explaination:
- Before Index: The database performs a Full Table Scan → checks every row in the table to find department = 'IT'.
- After Index: The database uses Index Seek on
idx_department → directly jumps to the rows where department = 'IT', skipping irrelevant data.
Syntax:
CREATE INDEX index_nameON table_name (column1, column2, ...);
- CREATE INDEX → Command to create a new index.
- index_name → User-defined name for the index.
- ON table_name → Specifies the table where the index will be created.
- (column1, column2, ...) → Columns on which the index is created. (Often used on columns in
WHERE, JOIN, or ORDER BY clauses for faster lookups).
Diagram of Index Optimization
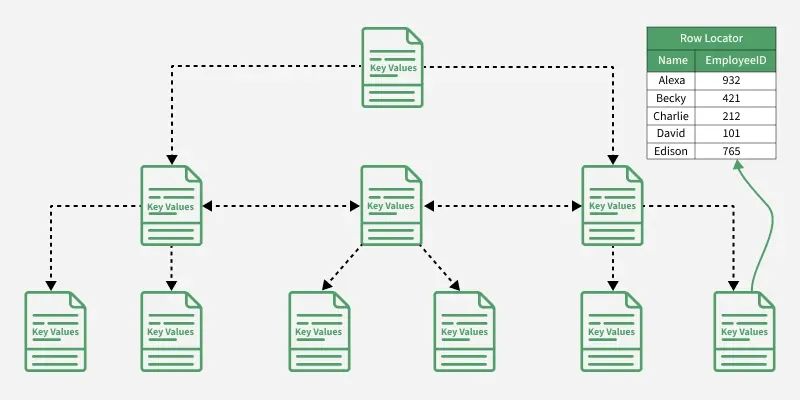 index optimization
index optimization Explain the diagram
- The diagram shows a B-Tree index structure used in SQL for fast data retrieval.
- The top node is the root, storing key values that guide the search.
- Intermediate nodes act like roadmaps, directing to the correct leaf node.
- Leaf nodes hold actual key values with row locators pointing to the exact table rows (like EmployeeID).
Explore
Basics
Queries & Operations
SQL Joins & Functions
Data Constraints & Aggregate Functions
Advanced SQL Topics
Database Design & Security