A recursive join in SQL is used to handle hierarchical data like employee-manager or parent-child relationships by repeatedly joining a table with itself. It is done using recursive CTEs, which run the query multiple times to retrieve all related levels of data.
Syntax:
WITH RECURSIVE cte_name AS (
-- Anchor Query: Select the root or starting point
SELECT columns
FROM table
WHERE condition
UNION ALL
-- Recursive Query: Join the CTE with the table to fetch related data
SELECT t.columns
FROM table t
INNER JOIN cte_name cte ON t.column = cte.column
)
Example of Recursive Join in SQL
Let's understand Recursive Join in SQL with example. First, we create a demo SQL database and table, on which we will use the Recursive Join command.
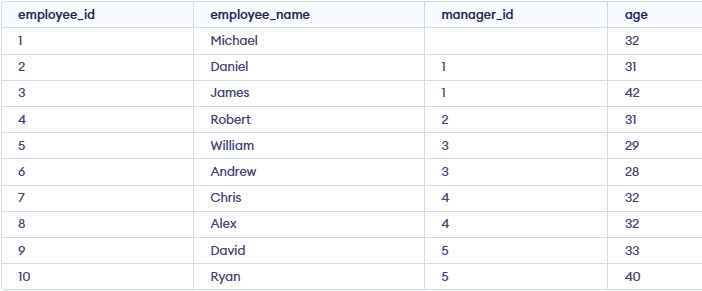
Now, we will use a recursive join to get a list of all employees and their managers, starting with Ankit (employee with employee_id = 1).
Query:
WITH RECURSIVE employee_hierarchy AS (
-- Anchor query: Start with Ankit (employee_id = 1)
SELECT employee_id, employee_name, manager_id, age
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id = 1
UNION ALL
-- Recursive query: Join the employees table with itself to get the employees reporting to each manager
SELECT e.employee_id, e.employee_name, e.manager_id, e.age
FROM employees e
INNER JOIN employee_hierarchy eh ON e.manager_id = eh.employee_id
)
SELECT * FROM employee_hierarchy;
Output:
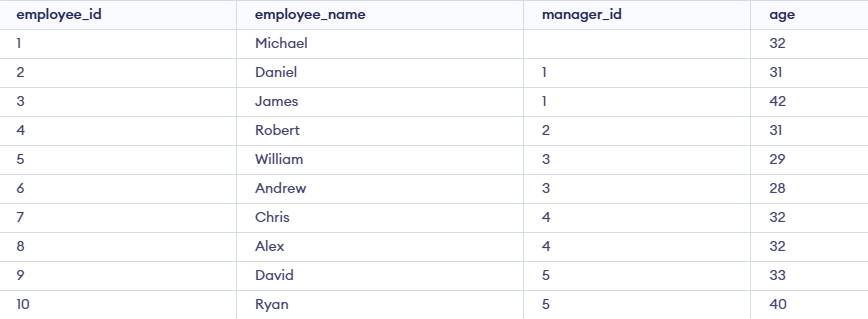
Explanation:
- The anchor part selects Ankit as the starting point.
- The recursive part joins the employees table with the employee_hierarchy CTE to find all employees who report to the previous level of employees.
- The process repeats until all employees who report to Ankit (and indirectly to others) are listed.
Applications of Recursive Joins
Here are the applications of recursive joins:
- Hierarchical Data Representation: Recursive joins are commonly used to represent and query hierarchical structures, such as employee-manager relationships, organizational charts, and bill of materials.
- Parent-Child Relationships: Recursive queries help retrieve data that represents parent-child relationships, such as categories and subcategories in a product catalog.
- Graph Traversal: Recursive joins are also used for traversing graphs or networks, such as social networks or transportation networks.
Explore
Basics
Queries & Operations
SQL Joins & Functions
Data Constraints & Aggregate Functions
Advanced SQL Topics
Database Design & Security