SQL CREATE INDEX Statement
Last Updated :
22 Nov, 2025
The CREATE INDEX statement in SQL is used to create indexes on tables to speed up data retrieval. Indexes work in the background to improve query performance and overall database efficiency.
Example: First, we create a demo SQL database and table, on which we use CREATE INDEX command.
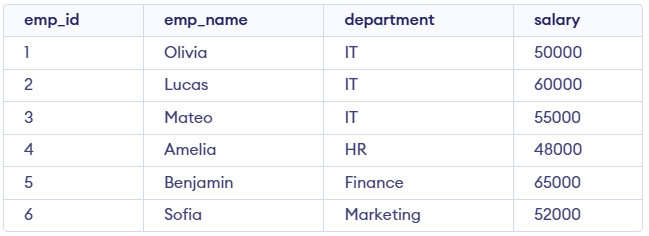 employees Table
employees TableQuery:
CREATE INDEX idx_employees_department
ON employees(department);
SELECT emp_name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE department = 'IT';
Output:

The CREATE INDEX command enables us to create an index on a table, improving query performance by providing a faster way to retrieve rows.
Syntax:
CREATE INDEX index_name
ON table (column1, column2.....);
- index_name: The name of the index.
- table_name: The name of the table on which the index is created.
- column1, column2, ...: The columns that the index will be applied to.
Creating a Unique Index:
A unique index ensures that all values in the indexed columns are unique preventing duplicate values.
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX index_name
ON table (column1, column2.....);
Example of SQL CREATE INDEX Statement
Let’s look at an example where we use the CREATE INDEX command on a Students table given below
 Students Table
Students TableStep 1: Create an Index
In this example, we will create an index on the name column of the Students table to speed up queries that search by name.
Query:
CREATE INDEX idx ON
Students(NAME);
--Creating a Unique Index
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX idx_student_id ON
Students(student_id);
Explanation:
- The first query creates a non-unique index on the NAME column to speed up search and sorting operations.
- The second query creates a unique index on student_id to prevent duplicate values and maintain data integrity.
Step 2: Retrieve Data Using the Index
After creating the index, queries that use the name column in their WHERE clause will benefit from the faster data retrieval provided by the index. The USE INDEX hint directs the query to use the idx_name index to speed up data retrieval.
Query:
SELECT * FROM STUDENTS USE INDEX(idx);
Output:

Step 3: Verifying the Index Creation
We can view all the indexes in a database to understand which ones are in use and confirm their structure. In SQL, the following query helps us see the indexes for a given table:
Syntax:
SHOW INDEXES FROM Students;
Output:

- Shows the list of indexes available on the table.
- Indicates one non-unique index on name and one unique index on student_id.
What is the purpose of CREATE INDEX?
Explanation:
Indexes function as quick-access structures that reduce the need for full table scans during searches.
What does a UNIQUE index ensure?
Explanation:
The UNIQUE index property ensures that no duplicate values can be inserted into the indexed column.
What does SHOW INDEXES FROM table_name display?
Explanation:
SHOW INDEXES displays all available indexes created on the specified table.
Which statement correctly creates a unique index?
-
CREATE INDEX UNIQUE idx ON table(col);
-
B. CREATE UNIQUE INDEX idx ON table(col);
-
C. UNIQUE INDEX CREATE idx table(col);
-
D. ADD UNIQUE INDEX idx table(col);
Explanation:
A unique index is created using CREATE UNIQUE INDEX followed by the index name and column list.
Why might an index be created on multiple columns?
-
-
-
-
To speed up multi-column searches
Explanation:
Creating an index on specific columns enhances the performance of queries that filter or sort data based on those columns.
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/5
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/5
1/5
< Previous
Next >
Explore
Basics
Queries & Operations
SQL Joins & Functions
Data Constraints & Aggregate Functions
Advanced SQL Topics
Database Design & Security