SQL CREATE VIEW Statement
Last Updated :
21 Nov, 2025
The SQL CREATE VIEW statement creates a virtual table based on a SELECT query. It does not store data itself but displays data from one or more tables when accessed.
- Simplifies complex SQL queries
- Improves data security by restricting column access
- Makes reporting and repeated queries easier to manage
Syntax:
CREATE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
- CREATE VIEW view_name: Creates a view with the specified name.
- AS: Indicates that the view will be defined based on the following SELECT query.
- SELECT column1, column2…: Columns included in the view (can be from one or multiple tables).
- FROM table_name: Table(s) from which the view will fetch data.
- WHERE condition: Optional filter to restrict the data included in the view.
Examples of SQL CREATE VIEW Statement
The CREATE VIEW statement in SQL is used to create a virtual table based on the result of a query. Views help simplify complex queries and enhance security by restricting access to specific columns or rows.
Example 1: Creating a Simple View
Consider the table products having three columns product_id, product_name, and price. Suppose we have to create a view that contains only products whose prices are greater than $50.

Query:
CREATE VIEW expensive_products AS
SELECT product_id, product_name, price
FROM products
WHERE price > 100;
Output:

- We develop a view called expensive_products.
- The view obtains columns product_id, product_name, and price from table products.
- We filter it so that it only includes rows with prices bigger than $100.
Example 2: Creating a Joined View
Assume that we have two tables employees and departments. We need to build a view combining information about both tables in order to show each employee’s name along with their department name:
Query:
CREATE VIEW employee_department_info AS
SELECT e.employee_id, e.first_name, e.last_name, d.department_name
FROM employees e
JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id;
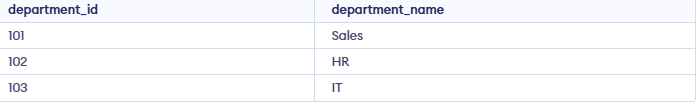
Employees table:

Departments table:
Query:
CREATE VIEW employee_department_info AS
SELECT
e.employee_id,
e.first_name,
e.last_name,
d.department_name
FROM employees e
JOIN departments d
ON e.department_id = d.department_id;
Output:
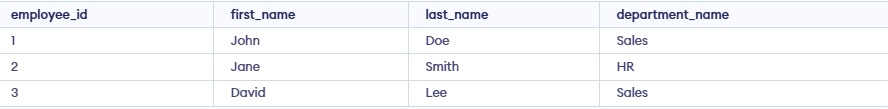
Explanation:
- A view named employee_department_info is created by us.
- Columns employee_id, first_name, last_name from employees table along with department_name from departments table are selected by this view.
- An inner join between employees and departments on department_id is performed to get department name for each employee.
Now when querying the employee_department_info view we shall have a list of employees together with their corresponding department names.
Explore
Basics
Queries & Operations
SQL Joins & Functions
Data Constraints & Aggregate Functions
Advanced SQL Topics
Database Design & Security