SQL CROSS JOIN creates a Cartesian product of two tables, meaning it returns every possible combination of rows from both tables. It does not use a join condition, and the total number of rows in the result is the number of rows in the first table multiplied by the number of rows in the second table. It is useful for generating all combinations of data.
 CROSS JOIN
CROSS JOINSyntax:
SELECT * FROM table1
CROSS JOIN table2;
Examples of SQL CROSS JOIN
Before diving into queries, let’s create two sample tables: Customer and Orders. These tables will help us understand how CROSS JOIN combines data into multiple combinations.
 Customers
Customers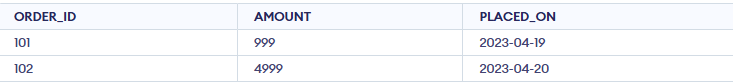 Orders
OrdersQuery:
SELECT *
FROM Customer
CROSS JOIN Orders;
Output:

Explanation: CROSS JOIN combines every row from the Customer table with every row from Orders table. Since there are 2 customers and 2 orders, result contains 2 × 2 = 4 rows.
What does a CROSS JOIN return?
-
Only matching rows from two tables
-
All rows from the first table only
-
All combinations of rows from both tables
-
Rows filtered by common column values
Explanation:
CROSS JOIN generates a Cartesian product, every row paired with every row.
What condition is required for a CROSS JOIN?
-
-
A join condition using ON
-
A WHERE clause must be used
-
Explanation:
CROSS JOIN does not use an ON condition; it simply pairs all rows.
If table A has 5 rows and table B has 3 rows, how many rows will a CROSS JOIN produce?
Explanation:
Total rows = 5 * 3 = 15 combinations.
What is a common use case for CROSS JOIN?
-
Removing duplicate values
-
Generating all possible combinations
-
Finding unmatched records
-
Filtering based on conditions
Explanation:
CROSS JOIN is ideal when you need every combination of two datasets.
What happens if both tables used in a CROSS JOIN are empty?
-
-
The result shows NULL for all columns
-
The result contains zero rows
-
The result contains one row
Explanation:
No rows × no rows = no combinations, so result is empty.
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/5
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/5
1/5
< Previous
Next >
Explore
Basics
Queries & Operations
SQL Joins & Functions
Data Constraints & Aggregate Functions
Advanced SQL Topics
Database Design & Security