Dropping a view removes only the view definition, not the actual data stored in the base tables. This makes it safe to delete views without affecting the original tables or their contents. The DROP VIEW command is commonly used when:
- Drop outdated views to keep the database clean.
- Remove unnecessary views to improve performance.
- Delete unused views to prevent unwanted data exposure.
- Maintain only required views for easier database management.
Example: Firstly, we create a demo table to implement the DROP VIEW command.
 Employees Table
Employees TableQuery:
-- Create a view
CREATE VIEW employee_view AS
SELECT id, name
FROM employees;
-- View data from the view
SELECT * FROM employee_view;
Output:
 employee_view
employee_view- CREATE VIEW employee_view AS ... creates a virtual table using the selected columns (id, name).
- SELECT * FROM employee_view; displays the data stored in the view.
-- Drop the view
DROP VIEW employee_view;
- DROP VIEW employee_view; deletes the view definition from the database.
- It does not delete or change the data in the original table.
Verifying the Deletion
To confirm the views have been successfully deleted, we can run the following query again. The employee_view should no longer appear in the result.
Query:
-- Check that the view is deleted or not
SELECT * FROM employee_view;
Error:

- The view was dropped using DROP VIEW, so it no longer exists.
- The SELECT query fails because the database can’t find employee_view.
Syntax:
DROP VIEW view_name;
Example: Implementation of DROP VIEW
This example shows creating a view first and then deleting it using the DROP VIEW command to remove the view definition from the database.
Creating Views
Consider the Employees table, which stores key employee details such as names, positions, salaries, and departments. Using CREATE VIEW, we can simplify queries and display only specific subsets of data in a clear and structured format.
 Employees Table
Employees Table1. View for High Salary Employees
The HighSalaryEmployees view filters the EMPLOYEES table to show only employees with a salary above 50,000, returning ID, Name, Position, Salary, and Department.
Query:
CREATE VIEW HighSalaryEmployees AS
SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE Salary > 50000;
Output:
 HighSalaryEmployees
HighSalaryEmployees2. View for Developers
The Developers view filters the Employees table to retrieve employees whose Position contains the word "Developer". The view returns the Name, Position, and Department of employees who have roles related to development within the IT department.
Query:
CREATE VIEW Developers AS
SELECT Name, Position, Department FROM EMPLOYEES WHERE Position LIKE '%Developer%';
Output:
 Developers
Developers3. View for Employees in IT Department
The ITEmployees view filters the Employees table to include only those employees who belong to the IT department. It retrieves all columns (ID, Name, Position, Salary, and Department) for employees working in the IT department, making it easier to query and manage IT-related employee data.
Query:
CREATE VIEW ITEmployees AS
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES WHERE Department = 'IT';
Output:
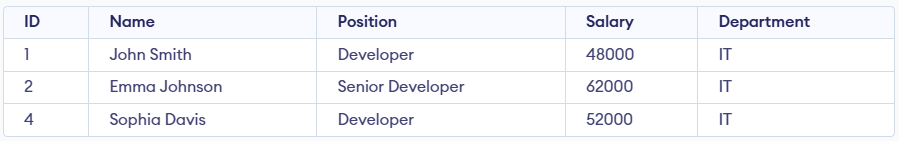 ITEmployees
ITEmployees
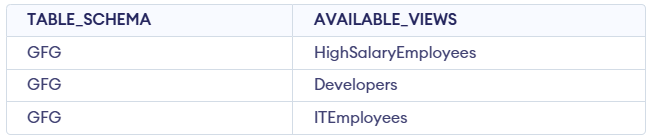
Query: To check the Created Views
SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME AS AVAILABLE_VIEWS
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.VIEWS
WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA='GFG';
To confirm that our views are created we can use the query mentioned above it will show us so our the views that we have created in form of table something like this:
Deleting a View
Once we no longer need a view, we can delete it using the DROP VIEW command. For example, let’s delete the HighSalaryEmployees and ITEmployees views.
Query:
DROP VIEW HighSalaryEmployees;
DROP VIEW ITEmployees;
- After executing this, these views will no longer exist in the database schema.
- We can confirm by querying the INFORMATION_SCHEMA.VIEWS table to see the remaining views.
Verifying the Deletion
To confirm the views have been successfully deleted, we can run the following query again. The HighSalaryEmployees and ITEmployees views should no longer appear in the result.
SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME AS AVAILABLE_VIEWS
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.VIEWS
WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA='GFG';
Output:

- This query retrieves information about views from the INFORMATION_SCHEMA.VIEWS table for a specific TABLE_SCHEMA ('GFG').
- It selects the TABLE_SCHEMA and EMPLOYEES columns from the VIEWS table, filtering the results to only include views from the 'GFG' schema.
Explore
Basics
Queries & Operations
SQL Joins & Functions
Data Constraints & Aggregate Functions
Advanced SQL Topics
Database Design & Security