Competitive edge practical guide to implement continuous improvement - part one
- 2. Practical Guide to ImplementPractical Guide to Implement Continuous Improvement andContinuous Improvement and Lean Six Sigma TechniquesLean Six Sigma Techniques Jose Villanueva Alcedo,Jose Villanueva Alcedo, M.B.A./T.M.M.B.A./T.M. Worldwide-Published AuthorWorldwide-Published Author
- 3. Practical Guide to ImplementPractical Guide to Implement Continuous Improvement andContinuous Improvement and Lean Six Sigma TechniquesLean Six Sigma Techniques PART ONE – Modules 1,2,3PART ONE – Modules 1,2,3 Presented byPresented by Jose Villanueva Alcedo,Jose Villanueva Alcedo, M.B.A./T.M.M.B.A./T.M. Worldwide-Published AuthorWorldwide-Published Author
- 4. Module One YouKaizen.com Deming’s Philosophy - Third Wave of theDeming’s Philosophy - Third Wave of the Industrial RevolutionIndustrial Revolution
- 5. Module One YouKaizen.com CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENTCONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT Solid Foundation of 3 Ts Never-ending improvement
- 6. System of Profound KnowledgeSystem of Profound Knowledge Deming 14-Point MethodologyDeming 14-Point Methodology Module One YouKaizen.com Revolutionized the WesternRevolutionized the Western Management MethodsManagement Methods & Practices& Practices
- 7. Appreciation for a System Theory of Knowledge Knowledge of Variation Knowledge of Psychology Module One YouKaizen.com The success of the whole organization is dependent on the leaders’ capability to orchestrate the delicate balance of each component for the optimization of the entire system
- 8. Whole and complex Clearly defined and shared goals Everyone must share a distinct commitment to aim the common goal Team-based environment Optimize the whole system Win-win result for all, as one team Module One YouKaizen.com All parts of the system are related
- 9. Being part of the whole Large number of participants and interactions Collaboration Interconnecting components Interdependence Optimizing the whole, not one part Module One YouKaizen.com Interdependent parts
- 10. Interdependence of all system components Module One YouKaizen.com All system components must operate interdependently in order to be efficient in business operation.
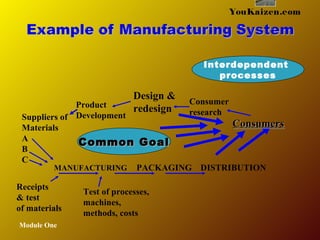
- 11. MANUFACTURING PACKAGING DISTRIBUTION ConsumersConsumers Consumer research Design & redesign Suppliers of Materials A B C Receipts & test of materials Test of processes, machines, methods, costs Module One YouKaizen.com Product Development Interdependent processes Common GoalCommon Goal
- 13. How we learn things How we use data-based knowledge Translate knowledge to action Module One YouKaizen.com
- 14. Module One YouKaizen.com Variety is good Variation is bad Variety vs. Variation
- 15. Module One YouKaizen.com •No two things are exactly alike, •not people •not processes •Processes vary because of its variation •Variation is a natural occurrence •Variation is inherent in life The Goal of Continuous Improvement is to reduce the range of variation.
- 16. Signal of process behaviorSignal of process behavior Process vary due to its variationProcess vary due to its variation Variation is a natural occurrenceVariation is a natural occurrence Identify causes of variationIdentify causes of variation Reduce the range of variation overReduce the range of variation over timetime 85% of variation due to chance85% of variation due to chance 15% of variation due to assignable15% of variation due to assignable causescauses Module One YouKaizen.com
- 17. People’s needsPeople’s needs Intrinsic motivationIntrinsic motivation Hierarchy of needs (Maslow)Hierarchy of needs (Maslow) Physiological, Safety, Love, Esteem, Self-Physiological, Safety, Love, Esteem, Self- actualizationactualization Leader’s guidance to see level ofLeader’s guidance to see level of needneed Module One YouKaizen.com
- 18. The hierarchy of needsThe hierarchy of needs Module One Physiological Safety Love Esteem Self-actualization YouKaizen.com Maslow’s Need TheoryMaslow’s Need Theory
- 19. 1. Create a constancy of purpose toward improvement of product and service 2. Adopt a new philosophy 3. Cease dependence on inspection to achieve quality 4. End the practice of awarding business on the basis of price tag. Instead minimize total costModule One YouKaizen.com Strategy of creating an environment of trust and teamwork within the organization.
- 20. 5. Improve constantly and forever, every process for planning, production, and service 6. Institute training on the job 7. Adopt and institute leadership 8. Drive out fears so that everyone may work effectively for the company Module One YouKaizen.com Strategy of constant unending improvement for everyone
- 21. 9. Break down barriers between departments 10. Eliminate slogans, exhortations, and targets for the work force 11. Eliminate work standards (quotas) on the factory floor and numerical goals for management Module One YouKaizen.com Remove the barriers All in one team, focus on processes, then improve processes, and the results should follow.
- 22. 12. Remove barriers that rob people of pride of workmanship 13. Institute a vigorous program of education and self- improvement for everyone 14. Put everybody in the company to work to accomplish the transformation Module One YouKaizen.com
- 24. • Kaizen is a Japanese name - kai = change, zen = good • Continuous Improvement Philosophy Initially taught in U.S.A. • Deming and Juran -Taught in Japan after World War II YouKaizen.com Module Two
- 25. • Way of thinking applied in all work • Focuses on continually improving the processes and systems first • Produce products and services that meet or exceed customer’s satisfaction YouKaizen.com Module Two
- 26. Time Improvement $ Ideal Pattern from Innovation $ $ Innovation I Innovation II Innovation III (Std) (Std) (Std) YouKaizen.com Module Two
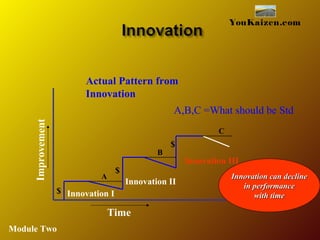
- 27. Time Improvement $ Actual Pattern from Innovation $ $ Innovation II Innovation III A B C A,B,C =What should be Std Innovation I YouKaizen.com Innovation can declineInnovation can decline in performancein performance with timewith time Module Two
- 28. Time Improvement $ Innovation plus Kaizen Innovation I Innovation II Kaizen $ Kaizen YouKaizen.com Fostering Innovation with Continuous Improvement Module Two
- 30. SCIENCE TECHNOLOGY DESIGN PRODUCTION DISTRIBUTION INNOVATION KAIZEN YouKaizen.comModule Two
- 31. Kaizen Innovation Gradualist approach Great-leap approach Small improvement Innovation Uses seven tools of Quality No tools Concerned more with processes Concerned more with results YouKaizen.com Module Two
- 32. Kaizen Innovation Improvement is slow, measures process activities Measures profit Close connection between Development, Design and Production No collaboration among departments KAIZEN speaks with Data Speaks with intuition, gut feel YouKaizen.com Module Two
- 33. Kaizen Innovation People - oriented Innovation – technology, money oriented Uses structured problem solving PDCA process No problem solving tools Covers Design, Production and Distribution Covers Science, Technology and Design YouKaizen.com Module Two
- 34. YouKaizen.com • SWOT Analysis • Integrate Continuous Improvement into Business Plan • Have short term and long term goals • Core competencies • Identify key processes and resources • Project management time line • Focus on improving Input, Process, Output • Cash Flow projection • Cost Benefit Analysis • Strategic Plan for Sustainability Strategic Advantage If your business does notIf your business does not have a Business Plan, it canhave a Business Plan, it can go somewhere else.go somewhere else. Module Two
- 35. YouKaizen.com Masaahi Imai (1986) in his book, Kaizen, explained: Key to Japan’s competitive success is Kaizen – Continual Improvement -gradual, unending improvement broken down into: • Management-oriented Kaizen • Group –oriented Kaizen • Individual-oriented Kaizen Module Two
- 36. Time YouKaizen.com Goal: College &NFL Football Runningback Zae ALCEDO #44 - 2nd Year High School Scholar at Campbell Hall, North Hollywood, Calif. Fostering his God-given Talents with Continuous Improvement Techniques By Team Effort with his dad Milestones Module Two
- 37. YouKaizen.com TBM Consulting Group Inc. (Quality Progress -April 1997) Survey of Kaizen programs based on four continents, Kuantan, Malaysia, to Sao Paulo, Brazil, to Raunheim, Germany, to Hot Springs, AR. Survey respondents that practice lean: • 64% reported lead times on product production • 63% were able to hold down or decrease product pricing • 61% experienced increased market share • 39% reduced the time required to launch new products • 24% were able to increase diversity of their product lines Module Two
- 38. YouKaizen.com Basic Statistics, Mark J. Kiemele, Stephen R. Schmidt, 1993, Air Academy Press Huge savings: Ford Motor Co. • Increased market share and profit • 65% reduction in customer reported defects • 35% increase in customer satisfaction Xerox • Manufacturing costs down 20% (1982 – 1986) • Cycle Time reduced by 60% • Revenue produced per employee up 20% Module Two
- 39. YouKaizen.com Basic Statistics, Mark J. Kiemele, Stephen R. Schmidt, 1993, Air Academy Press Huge savings: Westinghouse Electric Corp/Commercial Nuclear Fuel Division • Increased increased manufacturing by over 37% • Reduced scraps, rework, and manufacturing cycle time Hewlett Packard (Yokohama) • Profit up 244% from 1977-1984 • Hardware failure rates down 79% • Manufacturing costs down 42% • Productivity up 120% • Market share up 19% Module Two
- 40. YouKaizen.com Basic Statistics, Mark J. Kiemele, Stephen R. Schmidt, 1993, Air Academy Press Huge savings: Boeing Aerospace Co. For the Initial Upper Stage Program: • Billing errors reduced 0% • Cycle time reduced from 20 days to 3 • Technical order processing streamlined – saving $875 and 3.75 man-hours per O.T. • For the AWACS contract, billing delinquencies reduced by 50% • Overall Savings: $1.5 million per year Pittron Steel Foundry • Sales increased by 400% • Profits up by 30% • Productivity up 64% Module Two
- 41. YouKaizen.com Basic Statistics, Mark J. Kiemele, Stephen R. Schmidt, 1993, Air Academy Press Huge savings: U.S. Navy F-14 Overhaul Program: • Cut average cost from$1.6 million per aircraft in 1986 to $1.2 million in 1989 Cherry Point: • Aircraft failure rates reduced by 90% (1987-1988) Overhaul of USS Saratoga: • Expected to save $10 million and 22,000 man-days Norfolk Naval Shipyard: • Reduced rejection rate in electronic connectors from 55% to 6% Internal Revenue Service • Processing errors reduced from 30,000 (1986) to 3,000 (1987) Module Two
- 42. YouKaizen.com Basic Statistics, Mark J. Kiemele, Stephen R. Schmidt, 1993, Air Academy Press Huge savings: U.S. Navy F-14 Overhaul Program: • Cut average cost from$1.6 million per aircraft in 1986 to $1.2 million in 1989 Cherry Point: • Aircraft failure rates reduced by 90% (1987-1988) Overhaul of USS Saratoga: • Expected to save $10 million and 22,000 man-days Norfolk Naval Shipyard: • Reduced rejection rate in electronic connectors from 55% to 6% Internal Revenue Service • Processing errors reduced from 30,000 (1986) to 3,000 (1987) Module Two
- 43. YouKaizen.com Basic Statistics, Mark J. Kiemele, Stephen R. Schmidt, 1993, Air Academy Press Huge savings: Social Security Administration • Claim processing reduced to 73.9 days in 1987 from 81 days in 1986 Department of Housing and Urban Development • Average time to process a loan for property improvement and purchase of manufactured housing was 85 days (1985), 29 days (1986), and 22 days (1987) Massachusetts General Hospital • Improved the billing process by reducing monthly defects by 52%, resulting in projected $189,000 savings per year Module Two
- 44. YouKaizen.com Huge savings: 9/11/12: “ I was fortunate enough to work with Joe for twenty years. He has Excellent work ethics and a great set of values. Joe introduced and trained Pharmavite and me on Statistical Process Control, Continuous Improvement, Lean Best Practices and led the charge throughout the company. As an example, on one project, we reduced our lead time by 83%.” William D. Cottrell, CEO/Principal, Cottrell Consulting Supply Chain and APICS Professional __________________________________________________________________ Pharmavite, LLC, California: •Continuous Flow Process reduced manufacturing cycle time by 50% •Reduced inventory count from 7 to 2 days •Statistical Process Control, contract manufacturing from P&G Module Two
- 45. YouKaizen.com Huge savings: Pharmavite, LLC: • Soft Gelatin Polishing Cycle Time reduction by 60% • Six Sigma tablet weight vitamin savings and excellent product quality • Reduced errors in Batch Reports – resulting to reducing product release time by 40%. • Company-wide Team-based organizational transformation – strategic advantage through High Performance Teams throughout the enterprise, leveraged global market share Module Two
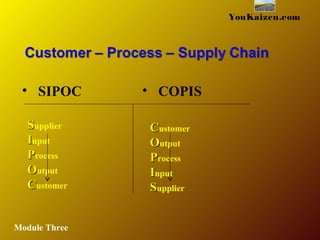
- 47. The key strategyThe key strategy Systems approach to changeSystems approach to change Process thinkingProcess thinking Success factorsSuccess factors Focus on the ProcessFocus on the Process Process modelProcess model SIPOC, COPISSIPOC, COPIS Variation in a ProcessVariation in a Process YouKaizen.com Module Three
- 48. Deming - based philosophy for maintaining the competitive advantage Processes Systems People Strategy which focuses on continuous improvement of all YouKaizen.com Module Three
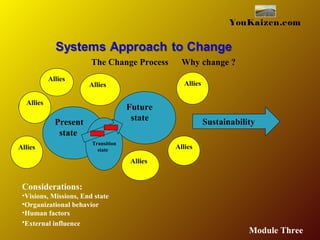
- 49. YouKaizen.com Present state The Change Process Transition state Future state Allies Allies Allies Allies Allies Allies Allies Why change ? Sustainability Considerations: •Visions, Missions, End state •Organizational behavior •Human factors •External influence Module Three
- 50. YouKaizen.com Goal: A. Integrate Continuous Improvement Technology Course into CPU Packaging Engineering and Business Administration Curriculum B. Implement Continuous Improvement in CPU Business Processes Module Three
- 51. YouKaizen.com Align with goals and reason for being: Where are we going What work should we do How do we get there Always keep our mission in mind Module Three
- 52. YouKaizen.com Continuous Improvement (CI) focuses on improving processes involving 4Ms: •Men (People) •Machines •Materials •Methods Module Three
- 53. YouKaizen.com Have a strategy: •Manage the direction: Focus on consistent direction. •Obtain the buy-in of the process managers and collaborate with them and the people in the whole system with a holistic vision to improve the Process. Module Three
- 54. YouKaizen.com Managing The Change Like steering a sailboat in turbulent water and stormy winds. If the wind is blowing at gale force dead broadside, you have to make a number of critical choices. The true sailor, knowing these choices works with the wind. Module Three
- 55. YouKaizen.com Leadership •Committed to satisfying customers •Increase ability to respond to change •Develop strategy •Define roles •Define goals •Provide resources •Lead by example •Provide training Module Three
- 56. YouKaizen.com Corporate culture: •Be obsessed with adding value for the customer •Support incremental improvement (individual own work, groups, teams) •Team-based culture transition Module Three
- 57. YouKaizen.com Attitudes: •Fully accept and internalize the need for CI •Involvement and pride in CI activities Module Three
- 58. YouKaizen.com Training: •Establish a training program •Awareness of employees’ role in CI •Raise capabilities and empowerment •Seven basic tools (Flowcharts, Pareto Diagrams, Cause & Effect Diagram, etc.) •Maximize effectiveness •Begin at the top and cascade down Module Three
- 59. YouKaizen.com Planning and Execution: •Select significant improvement opportunities •Phased step-by-step approach •Evaluate fine tuning vs. fundamental redesign •All in one team involvement •Cross functional •Multilevel •Involve the entire system (suppliers and customers) Module Three
- 60. YouKaizen.com Planning and Execution: •Coordinate activities •Project timeline •Ensure stable processes after each planned change •Evaluate change benefits •Make the change permanent Module Three
- 61. YouKaizen.com Continuous Improvement is to take a hard look at processes and reduce the variation in key business performance, first, before achieving the bottom-line. Module Three
- 62. YouKaizen.com Improve your process first, by reducing variation, then the results will follow. Competitive Edge – Practical Guide to Implement Continuous Improvement www.YouKaizen.com Module Three
- 63. - A blending of inputs to achieve the desired outputs PROCESS INPUTS OUTPUTS People Material Equipment Procedures Service Product Task YouKaizen.com Module Three
- 64. YouKaizen.com • SIPOC • COPIS SSupplier IInput PProcess OOutput CCustomer CCustomer OOutput PProcess IInput SSupplier Module Three
- 65. - Deming: 94% of the variation is due to chance causes/process which management has control, 6% is due to special causes. YouKaizen.com Module Three Demo of cards drop away from target is are caused by uncontrolled variations Targe t
- 66. Watch for Part Three dick of Slides with Modules 4, 5, and 6.
Editor's Notes
- #8: The road to Continuous Improvement requires leadership that is guided by Deming’s System of Profound Knowledge. This knowledge empowers a leader with the responsibility to implement a mindset of ongoing improvement. This theory says that the success of the whole organization is dependent on the leaders’ capability to orchestrate the delicate balance of each component, in order to optimize the whole system. Management or leader should orchestrate the implementation of the system of profound knowledge.
- #14: Theory of knowledge is how we learn things. Applied in Continuous Improvement methods, it is important to gain knowledge about the process through data of variation, whether variation is common-cause of special-cause. This knowledge dramatically affects decisions and direct improvement actions. A signal indicating that a variation is special caused warrants an investigation as to what occurred for a specific data point. However, when variation is common-caused and the desired result is not obtained, something needs to be done differently within the process, to improve it.
- #15: Variation is the signal to do or not do something on the process. No two things are exactly alike, not people, not processes. Processes vary because of its variation. Variation is a natural occurrence, and is inherent in life. The goal of continuous improvement is to reduce the range of variation over time, in addition to adjust the process level to the desired state.
- #16: Variation is the signal to do or not do something on the process. No two things are exactly alike, not people, not processes. Processes vary because of its variation. Variation is a natural occurrence, and is inherent in life. The goal of continuous improvement is to reduce the range of variation over time, in addition to adjust the process level to the desired state.
- #17: Variation is the signal to do or not do something on the process. No two things are exactly alike, not people, not processes. Processes vary because of its variation. Variation is a natural occurrence, and is inherent in life. The goal of continuous improvement is to reduce the range of variation over time, in addition to adjust the process level to the desired state.
- #18: Knowledge of Psychology is important in the system in order to know what motivates people. The leader that serves the people with vision and guidance to see the interconnectedness of the whole system can empower the people to share ownership identity. People are born with intrinsic motivation. Motivation is driven by peoples’ needs. Maslow’s principle established a hierarchy of needs…..
- #19: Though people are in a state of want all the time, according to Maslow’s theory, what they want is a function of the pattern of need satisfaction in the hierarchy. They can start out with lofty aspirations relative to love, esteem, and self-actualization, but be driven to more basic needs if those more basic needs become unsatisfied. As the lower-level needs are relatively satisfied, they become less directly motivating for behavior. One is motivated mainly by the next level of unsatisfied need. Since all managers attempt to influence human behavior, they must consider what needs are relatively unsatisfied, and hence can serve as levers for motivation.
- #23: This methodology, designed by Dr. Deming, sustains the organizations’ transformation to continuous improvement. It points out that the organization and the individual worker must work together, as a team, for a constant improvement of whatever they do.
- #28: Innovation without Continuous Improvement deteriorates after a while from what should be the standard.