Full Stack_Reac web Development and Application
- 1. Fundamentals of Web Design • Web design refers to the design of websites that are displayed on the internet. • It usually refers to the user experience aspects of website development rather than software development.
- 2. Web Page & Web Site Webpage Website Webpage consists of content regarding a single entity type Website constitutes content regarding several entities A direct URL link or a website can be used to access it A domain address is used to access it A combination of webpages is created using HTML and CSS Information is in HTML language An individual hypertext document linked under a website A collection of multiple pages hosted on the server Stores the contents or resources that are to be displayed on a website Is a place used to display the content
- 3. Webpage Website Comparatively, less complex More complex to develop Less time to develop Takes more time to develop The web page address of any specific website is directly dependent on the website address (domain). Webpage will not work if the domain is down Website address (domain) is independent of webpage address. If the webpage is deleted for any reason, the website will still continue to work. All other linked webpages will also work as usual Examples: Contact page, Registration Page, Service Page, About Us page and so on Examples: Flipkart.com, Nykaa.com, Amazon.com and more
- 4. Web Application • A Web application (Web app) is an application program that is stored on a remote server and delivered over the Internet through a browser interface. • Web services are Web apps by definition and many, although not all, websites contain Web apps.
- 6. Web Application Website Web application is designed for interaction with end users. Website basically contains static content. The user of web application can read the content of web application and also manipulate the data. The user of website only can read the content of website but not manipulate . The web application site should be precompiled before deployment. The website does not need to be precompiled . The function of a web application is quite complex. The function of website is simple.
- 7. Web Application Web Site Web application is interactive for users. Web site is not interactive for users. The browser capabilities involved with a web application is high. The browser capabilities involved with web site is high. Integration is complex for web application because of its complex functionality. Integration is simpler for web site. Web application mostly requires authentication In web site authentication is not necessary. EXAMPLE :- Amazon, Facebook, etc. EXAMPLE :- Breaking News, Aktu website, etc.
- 8. Client-Server Architecture • A client server application uses a two-tier architecture whereas a web application uses multi-tier architecture which consists of; user client, middle tier, and application server. • A web application uses a single-user system unlike a client server application which uses two users: client and server.
- 10. React JS
- 11. • React is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces. • React is used to build single-page applications. • React allows us to create reusable UI components. • React, sometimes referred to as a frontend JavaScript framework, is a JavaScript library created by Facebook. • React is a tool for building UI components.
- 12. How does React Work? • React creates a VIRTUAL DOM in memory. • Instead of manipulating the browser's DOM directly, React creates a virtual DOM in memory, where it does all the necessary manipulating, before making the changes in the browser DOM. • React only changes what needs to be changed! • React finds out what changes have been made, and changes only what needs to be changed.
- 13. React.JS History • Current version of React.JS is V18.0.0 (April 2022). • Initial Release to the Public (V0.3.0) was in July 2013. • React.JS was first used in 2011 for Facebook's Newsfeed feature. • Facebook Software Engineer, Jordan Walke, created it. • Current version of create-react-app is v5.0.1 (April 2022). • create-react-app includes built tools such as webpack, Babel, and ESLint.
- 14. React Getting Started • To use React in production, you need npm which is included with Node.js. • To get an overview of what React is, you can write React code directly in HTML. • But in order to use React in production, you need npm and Node.js installed.
- 15. Setting up a React Environment • If you have npx and Node.js installed, you can create a React application by using create-react- app. • If you've previously installed create-react- app globally, it is recommended that you uninstall the package to ensure npx always uses the latest version of create-react-app. • To uninstall, run this command: npm uninstall -g create-react-app.
- 16. • Run this command to create a React application named my-react-app: – npx create-react-app my-react-app
- 17. Run the React Application • Now you are ready to run your first real React application! • Run this command to move to the my-react- app directory: – cd my-react-app
- 18. • Run this command to run the React application my-react-app: – npm start • A new browser window will pop up with your newly created React App! If not, open your browser and type localhost:3000 in the address bar.
- 19. Render HTML
- 20. • React's goal is in many ways to render HTML in a web page. • React renders HTML to the web page by using a function called ReactDOM.render(). • The ReactDOM.render() function takes two arguments, HTML code and an HTML element. • The purpose of the function is to display the specified HTML code inside the specified HTML element. • But render where? • There is another folder in the root directory of your React project, named "public". In this folder, there is an index.html file. • You'll notice a single <div> in the body of this file. This is where our React application will be rendered.
- 21. import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'; ReactDOM.render(<p>Hello</p>, document.getElementById('root'));
- 22. import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'; const myelement = ( <table> <tr> <th>Name</th> </tr> <tr> <td>John</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Elsa</td> </tr> </table> ); ReactDOM.render(myele ment, document.getElement ById('root'));
- 23. React JSX
- 24. What is JSX? – JSX stands for JavaScript XML. – JSX allows us to write HTML in React. – JSX makes it easier to write and add HTML in React. Coding JSX • JSX allows us to write HTML elements in JavaScript and place them in the DOM without any createElement() and/or appendChild() methods. • JSX converts HTML tags into react elements. • You are not required to use JSX, but JSX makes it easier to write React applications.
- 25. import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'; const myElement = <h1>I Love JSX!</h1>; const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementB yId('root')); root.render(myElement);
- 26. import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'; const myElement = <h1>React is {5 + 5} times better with JSX</h1>; const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElement ById('root')); root.render(myElement);
- 27. import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'; const myElement = ( <ul> <li>Apples</li> <li>Bananas</li> <li>Cherries</li> </ul> ); const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')); root.render(myElement);
- 28. React Components
- 29. • Components are like functions that return HTML elements. • React Components • Components are independent and reusable bits of code. They serve the same purpose as JavaScript functions, but work in isolation and return HTML. • Components come in two types, Class components and Function components, in this tutorial we will concentrate on Function components.
- 30. Create Your First Component • When creating a React component, the component's name MUST start with an upper case letter. • Class Component • A class component must include the extends React.Component statement. This statement creates an inheritance to React.Component, and gives your component access to React.Component's functions. • The component also requires a render() method, this method returns HTML.
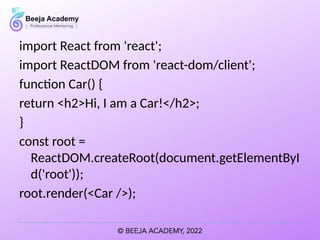
- 31. import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'; function Car() { return <h2>Hi, I am a Car!</h2>; } const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementByI d('root')); root.render(<Car />);
- 32. Components in Components function Car() { return <h2>I am a Car!</h2>; } function Garage() { return ( <> <h1>Who lives in my Garage?</h1> <Car /> </> ); } const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')); root.render(<Garage />);
- 33. Components in Files • This is the new file, we named it "Car.js": function Car() { return <h2>Hi, I am a Car!</h2>; } export default Car; • Now we import the "Car.js" file in the application, and we can use the Car component as if it was created here. import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'; import Car from './Car.js'; const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')); root.render(<Car />);
- 34. React Props
- 35. • Props are arguments passed into React components. • Props are passed to components via HTML attributes. • props stands for properties. React Props • React Props are like function arguments in JavaScript and attributes in HTML. • To send props into a component, use the same syntax as HTML attributes
- 36. import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'; function Car(props) { return <h2>I am a { props.brand }!</h2>; } const myElement = <Car brand="Ford" />; const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementB yId('root')); root.render(myElement);
- 37. function Car(props) { return <h2>I am a { props.brand }!</h2>; } function Garage() { return ( <> <h1>Who lives in my garage?</h1> <Car brand="Ford" /> </> ); } const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementByI d('root')); root.render(<Garage />);
- 38. React Events
- 39. • Just like HTML DOM events, React can perform actions based on user events. • React has the same events as HTML: click, change, mouseover etc. Adding Events – React events are written in camelCase syntax: – onClick instead of onclick. – React event handlers are written inside curly braces: – onClick={shoot} instead of onClick="shoot()". • React: – <button onClick={shoot}>Take the Shot!</button> • HTML: – <button onclick="shoot()">Take the Shot!</button>
- 40. function Football() { const shoot = () => { alert("Great Shot!"); } return ( <button onClick={shoot}>Take the shot!</button> ); } const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')); root.render(<Football />);
- 41. function Football() { const shoot = (a) => { alert(a); } return ( <button onClick={() => shoot("Goal!")}>Take the shot!</button> ); } const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')); root.render(<Football />);
- 43. if Statement function Goal(props) { const isGoal = props.isGoal; if (isGoal) { return <MadeGoal/>; } return <MissedGoal/>; } const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('r oot')); root.render(<Goal isGoal={false} />);
- 44. React Lists
- 45. function Car(props) { return <li>I am a { props.brand }</li>; } function Garage() { const cars = ['Ford', 'BMW', 'Audi']; return ( <> <h1>Who lives in my garage?</h1> <ul> {cars.map((car) => <Car brand={car} />)} </ul> </> ); } const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')); root.render(<Garage />);
- 46. function Car(props) { return <li>I am a { props.brand }</li>; } function Garage() { const cars = [ {id: 1, brand: 'Ford'}, {id: 2, brand: 'BMW'}, {id: 3, brand: 'Audi'} ]; return ( <> <h1>Who lives in my garage?</h1> <ul> {cars.map((car) => <Car key={car.id} brand={car.brand} />)} </ul> </> ); } const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')); root.render(<Garage />);











































![function Car(props) {
return <li>I am a { props.brand }</li>;
}
function Garage() {
const cars = ['Ford', 'BMW', 'Audi'];
return ( <> <h1>Who lives in my garage?</h1>
<ul>
{cars.map((car) => <Car brand={car} />)}
</ul>
</> );
}
const root =
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(<Garage />);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullstackreact-250219072345-63e2f2f4/85/Full-Stack_Reac-web-Development-and-Application-45-320.jpg)
![function Car(props) {
return <li>I am a { props.brand }</li>;
}
function Garage() {
const cars = [
{id: 1, brand: 'Ford'},
{id: 2, brand: 'BMW'},
{id: 3, brand: 'Audi'} ];
return (
<> <h1>Who lives in my garage?</h1>
<ul>
{cars.map((car) => <Car key={car.id} brand={car.brand} />)} </ul> </> );
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(<Garage />);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullstackreact-250219072345-63e2f2f4/85/Full-Stack_Reac-web-Development-and-Application-46-320.jpg)
