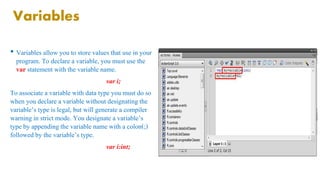
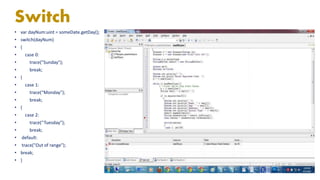
ActionScript is an object-oriented programming language developed by Macromedia (now Adobe) primarily for Adobe Flash Player, enhancing the capabilities of complex applications. The document discusses key concepts such as objects, classes, variables, data types, operators, conditionals, and functions essential for programming in ActionScript. It emphasizes that while ActionScript is not required for Flash content, it offers significant performance improvements and better code management options.