Lecture24 basiccircuits
- 2. Basic Circuits An electrical circuit is a closed path on which current flows. Current will not flow of the path is not closed (forming a circle). Breaking a circuit: Open circuit . The total sum of voltage differences in a circuit has to be 0. Why? Simplest circuit: battery & resistor
- 3. Resistances in Series Resistors in series all have the same current. Why? R in series have an equivalent resistance
- 4. Resistances in Series The sum of the voltages across each resistor equals the battery voltage. So: This formula is valid for any number of resistors in series.
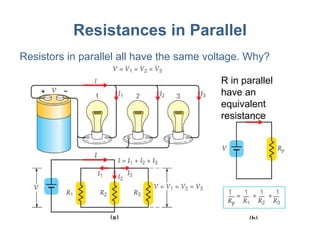
- 5. Resistances in Parallel Resistors in parallel all have the same voltage. Why? R in parallel have an equivalent resistance
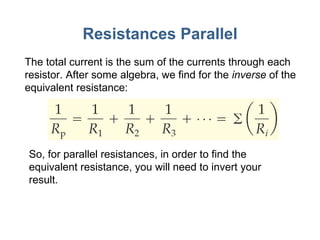
- 6. Resistances Parallel The total current is the sum of the currents through each resistor. After some algebra, we find for the inverse of the equivalent resistance: So, for parallel resistances, in order to find the equivalent resistance, you will need to invert your result.
- 7. Resistances in Series & Parallel The equivalent resistance of resistors in series is always greater than any individual resistance in the series. The equivalent resistance of resistors in parallel is always less than any individual resistance in the array.
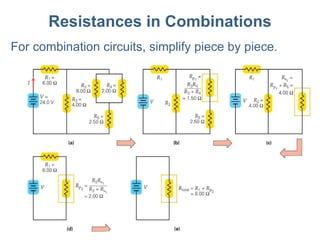
- 8. Resistances in Combinations For combination circuits, simplify piece by piece.
- 9. Applications Resistor divider Measuring voltages Providing correct voltage to a component
- 10. Multiloop Circuits Many circuits are not pure series-parallel combinations; more sophisticated tools are necessary to analyze them.
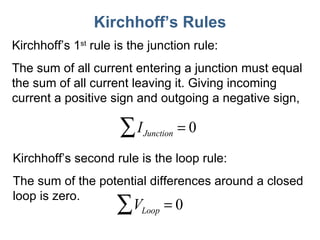
- 11. Kirchhoff ’s Rules Kirchhoff ’s 1 st rule is the junction rule: The sum of all current entering a junction must equal the sum of all current leaving it. Giving incoming current a positive sign and outgoing a negative sign, Kirchhoff ’s second rule is the loop rule: The sum of the potential differences around a closed loop is zero.
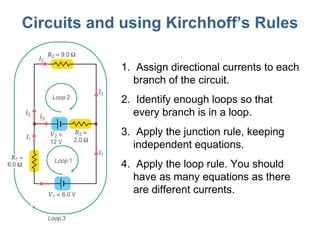
- 12. Circuits and using Kirchhoff ’s Rules Assign directional currents to each branch of the circuit. Identify enough loops so that every branch is in a loop. Apply the junction rule, keeping independent equations. Apply the loop rule. You should have as many equations as there are different currents.
- 13. Circuits and using Kirchhoff ’s Rules This example:
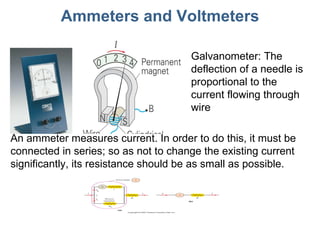
- 14. Ammeters and Voltmeters Galvanometer: The deflection of a needle is proportional to the current flowing through wire An ammeter measures current. In order to do this, it must be connected in series; so as not to change the existing current significantly, its resistance should be as small as possible.
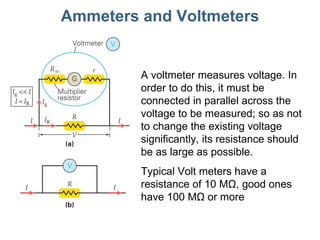
- 15. Ammeters and Voltmeters A voltmeter measures voltage. In order to do this, it must be connected in parallel across the voltage to be measured; so as not to change the existing voltage significantly, its resistance should be as large as possible. Typical Volt meters have a resistance of 10 MΩ, good ones have 100 MΩ or more
- 16. Ammeters and Voltmeters Multirange meters have a selection of shunt and multiplier resistors, to optimize the measurement of currents and voltages of different magnitudes.
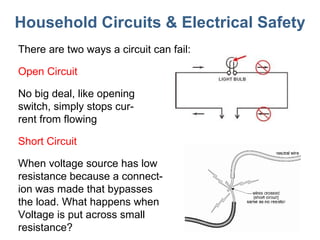
- 17. Household Circuits & Electrical Safety There are two ways a circuit can fail: Open Circuit No big deal, like opening switch, simply stops cur- rent from flowing Short Circuit When voltage source has low resistance because a connect- ion was made that bypasses the load. What happens when Voltage is put across small resistance?
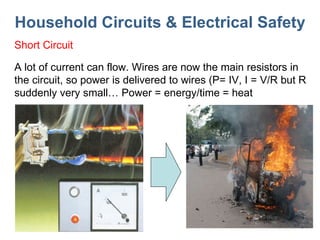
- 18. Household Circuits & Electrical Safety Short Circuit A lot of current can flow. Wires are now the main resistors in the circuit, so power is delivered to wires (P= IV, I = V/R but R suddenly very small… Power = energy/time = heat
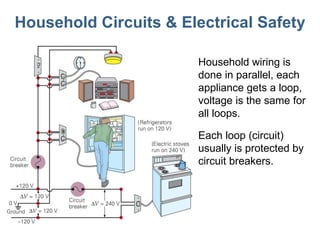
- 19. Household Circuits & Electrical Safety Household wiring is done in parallel, each appliance gets a loop, voltage is the same for all loops. Each loop (circuit) usually is protected by circuit breakers.
- 20. Household Circuits & Electrical Safety Circuit breakers are used in most newer homes. A bimetallic strip opens the circuit if the current becomes too high (like when there is a short circuit) If a circuit breaker trips, it can be reset. Bi-metallic strip bends because different materials expand different amounts when temperature goes up
- 21. Household Circuits & Electrical Safety Fuses are electrical components protecting a circuit. They are designed so the fuse strip melts and opens the circuit if the current exceeds a predetermined value. Fuses are rated for different currents; the fuse rating should always match the maximum allowable current in the circuit. When a fuse burns out, it must be replaced.
- 22. Household Circuits & Electrical Safety Sometimes, a person can provide lower resistance for current than the intended path in a circuit This is because circuits have one part of it connected to “ground”, to make that part of a circuit the same potential as the earth/environment. People are at ground potential. How can we do this? Why do we do this? In order to provide needed protection for people, the fuse or circuit breaker needs to be on the “hot” side of the circuit.
- 23. Household Circuits & Electrical Safety However, even on the hot side the fuse or breaker may not always protect the circuit. If an internal wire touches the conductive casing of an appliance, you can still get a shock. This can be avoided by using a dedicated ground line. You can tell which devices have such a line; they have 3-prong plugs.