
 Data Structure
Data Structure Networking
Networking RDBMS
RDBMS Operating System
Operating System Java
Java MS Excel
MS Excel iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C Programming
C Programming C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
- Who is Who
Print all internal nodes of a Binary tree in C++
In this problem, we are given a binary tree and we have to print all internal nodes of the binary tree.
The binary tree is a tree in which a node can have a maximum of 2 child nodes. Node or vertex can have no nodes, one child or two child nodes.
Example −
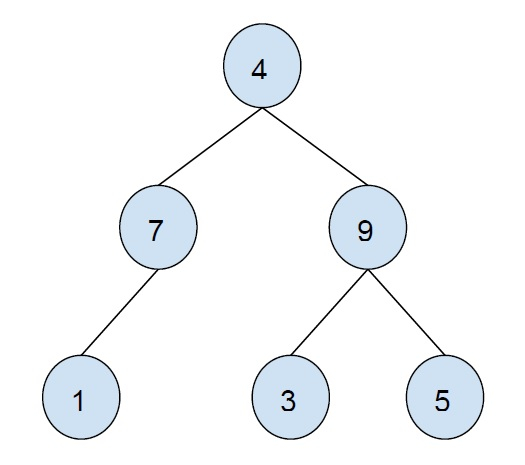
Internal Node is a node that can have at least one child i.e. non-leaf node is an internal node.
Let’s take an example to understand the problem −

Output − 7 4 9
To solve this problem, we will traverse the binary tree using BFS(breadth-first search) traversal.
While traversal we will push nodes to a queue. When we pop elements from the queue, we will print all nodes of the tree that do not have any child nodes.
Example
Our logic is implemented by the below code −
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left, *right;
Node(int data){
left = right = NULL;
this->data = data;
}
};
void printNonLeafNodes(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> treeNodes;
treeNodes.push(root);
while (!treeNodes.empty()) {
Node* curr = treeNodes.front();
treeNodes.pop();
bool isInternal = 0;
if (curr->left) {
isInternal = 1;
treeNodes.push(curr->left);
}
if (curr->right) {
isInternal = 1;
treeNodes.push(curr->right);
}
if (isInternal)
cout<<curr->data<<"\t";
}
}
int main() {
Node* root = new Node(43);
root->left = new Node(12);
root->right = new Node(78);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->right->left = new Node(9);
root->right->right = new Node(1);
root->right->right->right = new Node(50);
root->right->right->left = new Node(25);
cout<<"All internal Nodes of the binary tree are :\n";
printNonLeafNodes(root);
return 0;
}
Output
All internal Nodes of the binary tree are − 43 12 78 1

Advertisements
