
 Data Structure
Data Structure Networking
Networking RDBMS
RDBMS Operating System
Operating System Java
Java MS Excel
MS Excel iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C Programming
C Programming C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
- Who is Who
Print the First Shortest Root to Leaf Path in a Binary Tree in C++
Given the binary tree the program must find out the shortest path from the root to leaf amongst many given paths.
Since we traverse the tree from left to right, so if there are multiple shortest paths from the root to leaf than the program will print the first traversed the shortest path on the left side of a tree.
We can use a queue that will traverse each level using Level order traversal and the path with the least number of levels will be printed as it will be the shortest path from the root to leaf
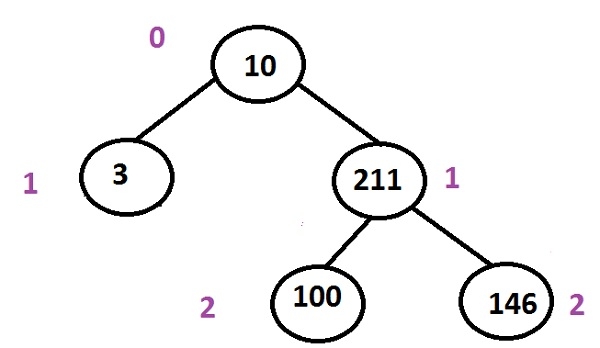
In the above tree, multiple paths from the root to leaf are
10 -> 3 (this one is the shortest path amongst all) 10 -> 211 -> 100 10 -> 211 -> 146
Example
Input : 10 3 211 100 146 Output : 10 3
Algorithm
Step 1 -> create a structure of a node as struct node struct node *left, *right int data End Step 2 -> function to create a node node* newnode(int data) node *temp = new node temp->data = data temp->left = temp->right= NULL return temp Step 3 -> create function for calculating path void path(int data, unordered_map <int,int> prnt) IF prnt[data] = data Return End path(prnt[data], prnt) print prnt[data] step 4 -> function for finding out the left path void left(Node* root) create STL queue<Node*> que que.push(root) int leaf = -1 Node* temp = NULL Create STL unordered_map<int, int> prnt prnt[root->data] = root->data Loop While !que.empty() temp = que.front() que.pop() IF !temp->left && !temp->right leaf = temp->data break End Else IF temp->left que.push(temp->left) prnt[temp->left->data] = temp->data End IF temp->right que.push(temp->right) prnt[temp->right->data] = temp->data End End End path(leaf, prnt) print leaf Step 5 -> In main() Create tree using Node* root = newnode(90) root->left = newnode(21) call left(root) stop
Example
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// structure of a node
struct Node {
struct Node *left,*right;
int data;
};
//function to create a new node
Node* newnode(int data){
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
//function to set a path
void path(int data, unordered_map <int,int> prnt) {
if (prnt[data] == data)
return;
path(prnt[data], prnt);
cout << prnt[data] << " ";
}
//function for a leaf path
void left(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
que.push(root);
int leaf = -1;
Node* temp = NULL;
unordered_map<int, int> prnt;
prnt[root->data] = root->data;
while (!que.empty()){
temp = que.front();
que.pop();
if (!temp->left && !temp->right{
leaf = temp->data;
break;
} else {
if (temp->left){
que.push(temp->left);
prnt[temp->left->data] = temp->data;
}
if (temp->right){
que.push(temp->right);
prnt[temp->right->data] = temp->data;
}
}
}
path(leaf, prnt);
cout << leaf << " ";
}
int main(){
Node* root = newnode(90);
root->left = newnode(21);
root->right = newnode(32);
root->left->left = newnode(45);
root->right->left = newnode(52);
root->right->right = newnode(27);
root->left->left->left = newnode(109);
root->left->left->right = newnode(101);
root->right->right->left = newnode(78);
left(root);
return 0;
}
Output
if we run the above program then it will generate the following output
90 32 52

Advertisements
