
 Data Structure
Data Structure Networking
Networking RDBMS
RDBMS Operating System
Operating System Java
Java MS Excel
MS Excel iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C Programming
C Programming C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
- Who is Who
Program to print root to leaf paths without using recursion using C++
In this tutorial, we will be discussing a program to print the path from the root node to all the leaf nodes in a given binary tree.
For example, let us say we have the following binary tree
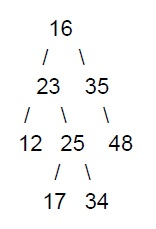
In this binary tree, we have 4 leaf nodes. Therefore we can have 4 paths from the root node to the leaf node.
To solve this, we will use the iterative approach. While doing preorder traversal of the binary tree we can store parent pointers in a map. Whenever during traversal we encounter a leaf node we can easily print its path from the root node using parent pointers.
Example
#include <bits/stdc++.h>>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
//to create a new node
Node* create_node(int data){
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
//printing the path from root to leaf
void print_cpath(Node* curr, map<Node*, Node*> parent){
stack<Node*> nodes_stack;
while (curr){
nodes_stack.push(curr);
curr = parent[curr];
}
while (!nodes_stack.empty()){
curr = nodes_stack.top();
nodes_stack.pop();
cout << curr->data << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//to perform pre order traversal
void preorder_traversal(Node* root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
stack<Node*> nodeStack;
nodeStack.push(root);
map<Node*, Node*> parent;
parent[root] = NULL;
while (!nodeStack.empty()){
Node* current = nodeStack.top();
nodeStack.pop();
if (!(current->left) && !(current->right))
print_cpath(current, parent);
if (current->right){
parent[current->right] = current;
nodeStack.push(current->right);
}
if (current->left){
parent[current->left] = current;
nodeStack.push(current->left);
}
}
}
int main(){
Node* root = create_node(101);
root->left = create_node(82);
root->right = create_node(23);
root->left->left = create_node(34);
root->left->right = create_node(55);
root->right->left = create_node(29);
preorder_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
Output
101 82 34 101 82 55 101 23 29

Advertisements
