Broken Access Control is a web security vulnerability that arises when an application fails to enforce restrictions on user permissions, allowing attackers to access data or perform actions beyond their authorized rights. An attacker can do:
- Viewing or modifying other users’ accounts.
- Accessing sensitive data (like personal details or financial info).
- Performing admin-level functions without authorization.
Example:
- If a normal user can change the URL from
/user/profile/101 to /user/profile/102 and access another person’s profile without authorization, it indicates a Broken Access Control vulnerability - This is considered one of the most critical web vulnerabilities as it can lead to data exposure, privilege escalation, and even complete account takeover.
 Broken Access Control
Broken Access ControlAccess control vulnerabilities
We can split access control vulnerabilities mainly into three categories:
1. Horizontal privilege escalation:
This occurs when users gain access to data or functionality belonging to other users who have the same level of permissions.
For example
When you log into your social media account, you are allowed to see your content and make changes to it, but you are not allowed to get access to other users' accounts. However, things could go wrong if access control is flawed.
2. Vertical privilege escalation:
This happens when a lower-privileged user (e.g., a regular user) is able to access data or perform actions reserved for higher-privileged roles (e.g., admins).
For example
To perform certain functions and reach certain resources, a user needs to have admin privileges, a regular user doesn't have such privileges. Broken vertical access controls let attackers get access to those functionalities.
3. Context-dependent privilege escalation:
This takes place when a user, due to being in a specific context (such as a certain page, workflow, or state), gains higher privileges than intended.
Example
Imagine an e-commerce website:
- A customer should only be able to add items to their own cart.
- But due to a flaw, if they change the cart ID in the request while on the "checkout" page, they can view or modify someone else’s cart.
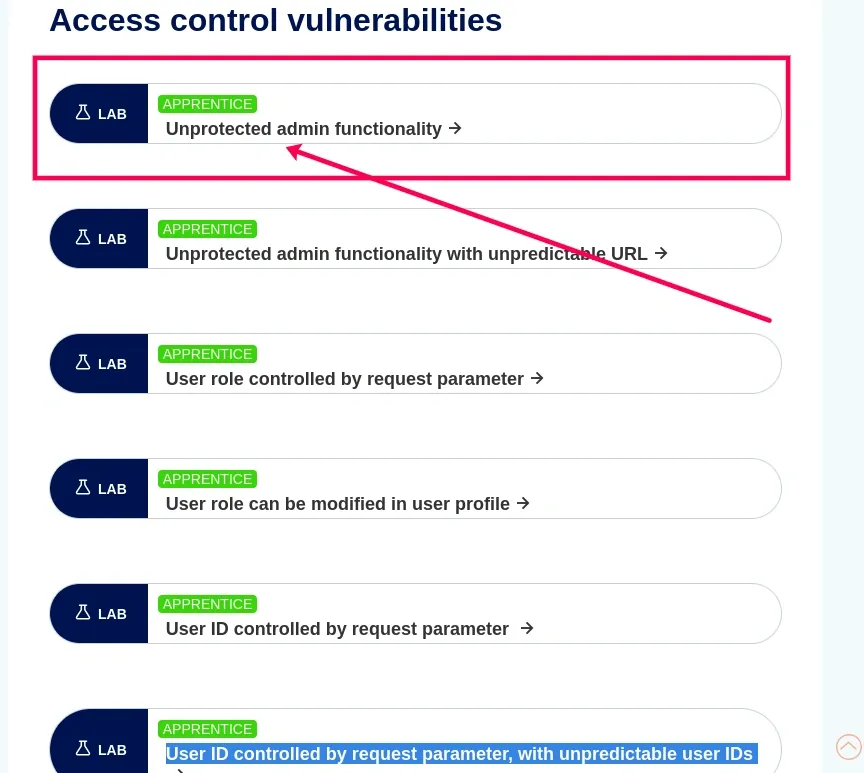
Hand On lab For broken Access Control
Given below the step by step hands-on lab of broken access control
Step 1. Access the Lab
- Open PortSwigger Academy.
- set up FoxyProxy extension to route traffic through Burp.
- Click on Home. It just redirects back to the main page.
- Click on My Account. It shows the login page (but no direct admin option is visible).

Step 3. Discover the Admin Panel
- Try accessing common admin panel paths in the URL:
/admin
/admin-panel
/administrator
/administrator-panel
https://0a8c003f03363823818d66c100140038.web-security-academy.net/administrator-panel
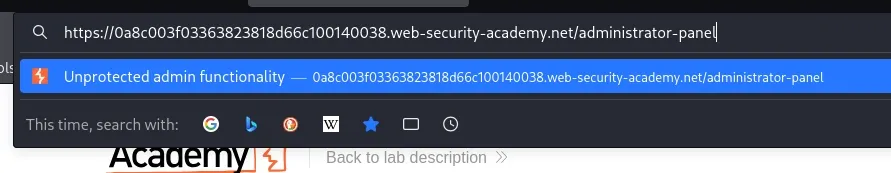
You’ll notice that /administrator-panel is accessible without authentication or restrictions.
Step 4. Access the Admin Panel

- The panel loads successfully, confirming the broken access control flaw.
Step 5. Delete the Target User
- Inside the admin panel, look for the “Delete user” function.
- Select the user carlos.
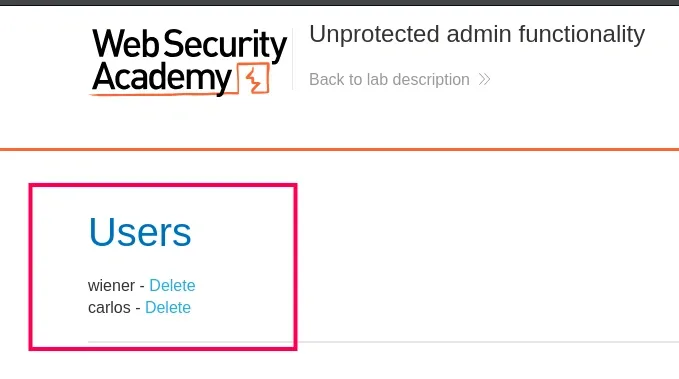
- Confirm deletion.
- The lab should now display the message: “Congratulations, you solved the lab!”.

Impacts of broken access control
The following are the major impacts of broken access control:
1. Unique User IDs and Your Data
Whenever we create an account on a website, the system assigns us a unique user ID. This ID is used to identify us and retrieve our personal data from the database.
For example, if your user ID is 986, your profile page URL might look like this:
https://brokenaccesscontrol.com/profile?id=986
Now, just like you, every other user also has their own unique ID. If the website does not enforce proper access control, you could change the number in the URL (for example, from 986 to 987) and view another user’s profile. This happens when access control is poorly implemented on the server, allowing users to access data that does not belong to them.
2. Exploiting Weak Access Controls
Hackers can exploit broken access control flaws to reach resources and services that should only be available to authorized users.
Example:
The admin page of a web application should only be accessible to administrators. Regular users should never be able to reach it. But if access control is poorly implemented, an attacker can simply tweak the URL and open the admin panel. Once inside, they could:
- Steal sensitive user data
- Delete or modify accounts
- Deploy malicious payloads that could compromise or even destroy the entire application and its hosting environment
Example Attack Scenarios
Here are two example attack scenarios that demonstrate how Broken Access Control can be exploited.
Scenario 1: Accessing another user’s account through URL parameters
Some applications directly use the data a user provides in a request without verifying it. For example:
Java
pstmt.setString(1, request.getParameter("acct"));
ResultSet results = pstmt.executeQuery();
If you’re logged in and your account number is in the URL, like this:
https://example.com/app/accountInfo?acct=12345
An attacker could simply change the number (acct=67890) to try and view someone else’s account information. If the application doesn’t check permissions properly, the attacker can see or even modify another user’s data.
Scenario 2: Accessing restricted admin pages
Websites often have different sections for different types of users, like regular users and administrators. For example:
https://example.com/app/getAppInfo
https://example.com/app/admin_getAppInfo
If the website doesn’t block unauthorized access, an attacker (or even a logged-in normal user) could try typing the admin page URL directly into the browser. If they can open it without being an admin, that’s a serious security flaw.
Explore
Computer Network Basics
Physical Layer
Data Link Layer
Network Layer
Transport Layer
Session Layer & Presentation Layer
Application Layer
Advanced Topics
Practice